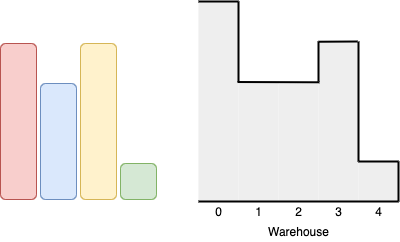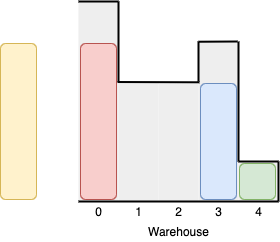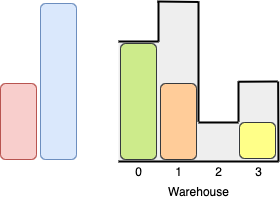| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
You are given two arrays of positive integers, boxes and warehouse, representing the heights of some boxes of unit width and the heights of n rooms in a warehouse respectively. The warehouse's rooms are labelled from 0 to n - 1 from left to right where warehouse[i] (0-indexed) is the height of the ith room.
Boxes are put into the warehouse by the following rules:
- Boxes cannot be stacked.
- You can rearrange the insertion order of the boxes.
- Boxes can only be pushed into the warehouse from left to right only.
- If the height of some room in the warehouse is less than the height of a box, then that box and all other boxes behind it will be stopped before that room.
Return the maximum number of boxes you can put into the warehouse.
Example 1:
Input: boxes = [4,3,4,1], warehouse = [5,3,3,4,1] Output: 3 Explanation:We can first put the box of height 1 in room 4. Then we can put the box of height 3 in either of the 3 rooms 1, 2, or 3. Lastly, we can put one box of height 4 in room 0. There is no way we can fit all 4 boxes in the warehouse.
Example 2:
Input: boxes = [1,2,2,3,4], warehouse = [3,4,1,2] Output: 3 Explanation:Notice that it's not possible to put the box of height 4 into the warehouse since it cannot pass the first room of height 3. Also, for the last two rooms, 2 and 3, only boxes of height 1 can fit. We can fit 3 boxes maximum as shown above. The yellow box can also be put in room 2 instead. Swapping the orange and green boxes is also valid, or swapping one of them with the red box.
Example 3:
Input: boxes = [1,2,3], warehouse = [1,2,3,4] Output: 1 Explanation: Since the first room in the warehouse is of height 1, we can only put boxes of height 1.
Constraints:
n == warehouse.length1 <= boxes.length, warehouse.length <= 1051 <= boxes[i], warehouse[i] <= 109
class Solution:
def maxBoxesInWarehouse(self, boxes: List[int], warehouse: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(warehouse)
left = [warehouse[0]] * n
for i in range(1, n):
left[i] = min(left[i - 1], warehouse[i])
boxes.sort()
i, j = 0, n - 1
while i < len(boxes):
while j >= 0 and left[j] < boxes[i]:
j -= 1
if j < 0:
break
i, j = i + 1, j - 1
return iclass Solution {
public int maxBoxesInWarehouse(int[] boxes, int[] warehouse) {
int n = warehouse.length;
int[] left = new int[n];
left[0] = warehouse[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
left[i] = Math.min(left[i - 1], warehouse[i]);
}
Arrays.sort(boxes);
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
while (i < boxes.length) {
while (j >= 0 && left[j] < boxes[i]) {
--j;
}
if (j < 0) {
break;
}
++i;
--j;
}
return i;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maxBoxesInWarehouse(vector<int>& boxes, vector<int>& warehouse) {
int n = warehouse.size();
int left[n];
left[0] = warehouse[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
left[i] = min(left[i - 1], warehouse[i]);
}
sort(boxes.begin(), boxes.end());
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
while (i < boxes.size()) {
while (j >= 0 && left[j] < boxes[i]) {
--j;
}
if (j < 0) {
break;
}
++i;
--j;
}
return i;
}
};func maxBoxesInWarehouse(boxes []int, warehouse []int) int {
n := len(warehouse)
left := make([]int, n)
left[0] = warehouse[0]
for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
left[i] = min(left[i-1], warehouse[i])
}
sort.Ints(boxes)
i, j := 0, n-1
for i < len(boxes) {
for j >= 0 && left[j] < boxes[i] {
j--
}
if j < 0 {
break
}
i, j = i+1, j-1
}
return i
}function maxBoxesInWarehouse(boxes: number[], warehouse: number[]): number {
const n = warehouse.length;
const left: number[] = new Array(n);
left[0] = warehouse[0];
for (let i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
left[i] = Math.min(left[i - 1], warehouse[i]);
}
boxes.sort((a, b) => a - b);
let i = 0;
let j = n - 1;
while (i < boxes.length) {
while (j >= 0 && left[j] < boxes[i]) {
--j;
}
if (j < 0) {
break;
}
++i;
--j;
}
return i;
}