-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 17
Prisma
Prisma is an open source ORM.
Object–Relational Mapping is a technique that allows you to query data from a database through an object oriented paradigm. That creates a virtual object database that can be used within the programming language.
Basically, Prisma allows you to work with a database using less lines of code, and with more convenient methods.
To set up a virtual database, you will need a schema file. A schema is the main config file for Prisma. It usually is called schema.prisma. Here is an example of one:
//This part connects you to your database
datasource db {
provider = "mysql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
}
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
email String @unique
name String?
role Role @default(USER)
posts Post[]
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
updatedAt DateTime @updatedAt
published Boolean @default(false)
title String @db.VarChar(255)
author User? @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int?
}
enum Role {
USER
ADMIN
}Prisma takes the models written in the schema. Then, it generates the SQL migrations and types stored in node_modules/.prisma/client. These types are aware of the relations that are created in the models as well as provide generated code that can be used to query the models. When you query using the client, it takes the queries and passes them to a Query Engine binary that optimizes it and converts it to a database query.
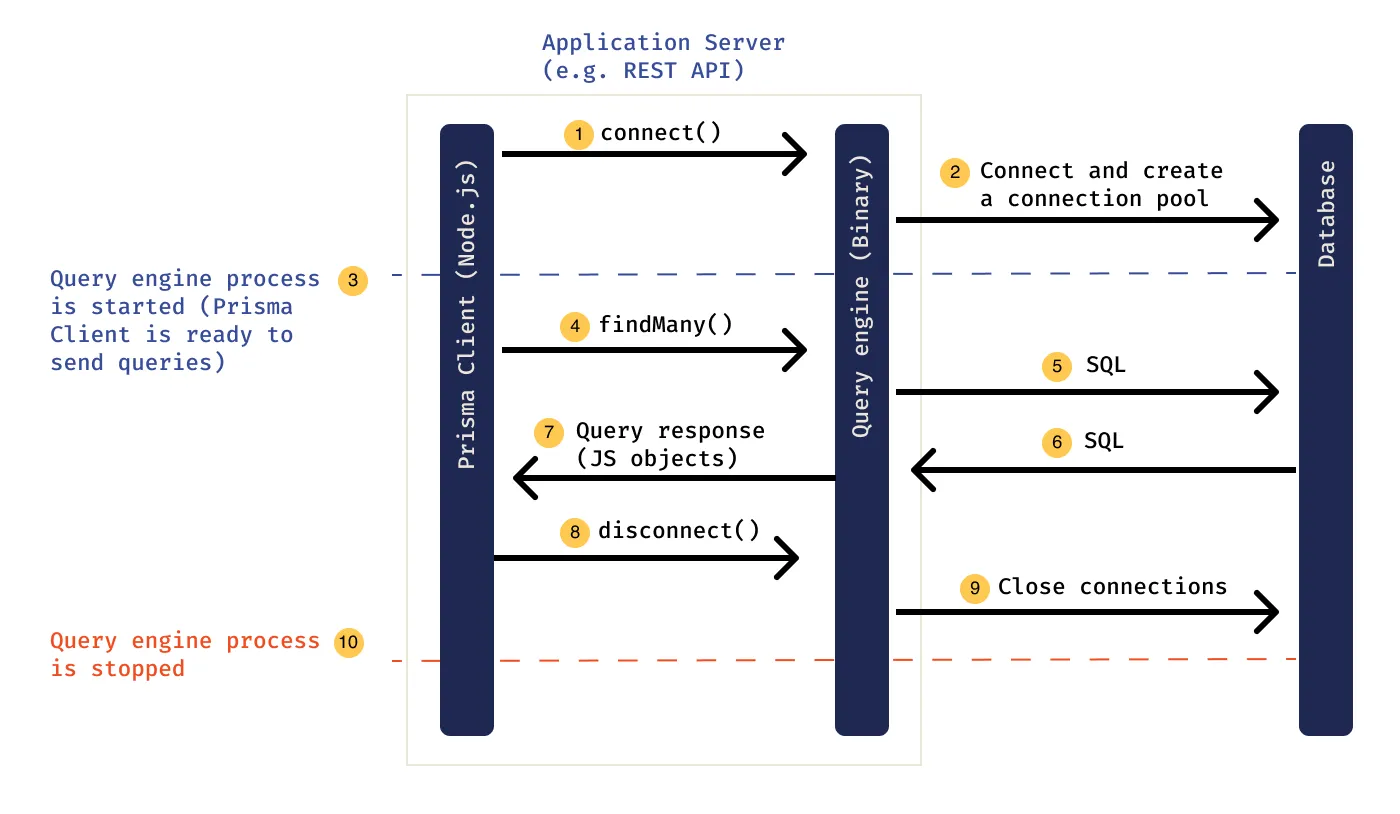
Prisma's engine is something you would not have to interact with ever when working with Prisma, but it helps us understand how Prisma works. All communication to the database layer happens via the engine.
Prisma's main goal is to make application developers more productive when working with databases. Here are a few examples of how Prisma achieves this:
- Thinking in objects instead of mapping relational data
- Queries not classes to avoid complex model objects
- Single source of truth for database and application models
- Healthy constraints that prevent common pitfalls and anti-patterns
- An abstraction that makes the right thing easy ("pit of success")
- Type-safe database queries that can be validated at compile time
- Less boilerplate so developers can focus on the important parts of their app
- Auto-completion in code editors instead of needing to look up documentation

For an existing SQL database
- an existing Node.js project with a
package.json - Node.js installed on your machine
- a MySQL database server running and a database with at least one table
Make sure you have your database connection URL (that includes your authentication credentials) at hand! If you don't have a database server running and just want to explore Prisma, check out the Quickstart.
As a first step, navigate into your project directory that contains the package.json file.
Next, add the Prisma CLI as a development dependency to your project:
npm install prisma --save-dev
You can now invoke the Prisma CLI by prefixing it with npx:
npx prisma
Next, set up your Prisma project by creating your Prisma schema file template with the following command:
npx prisma init
This command does two things:
- creates a new directory called
prismathat contains a file calledschema.prisma, which contains the Prisma schema with your database connection variable and schema models - creates the
.envfile in the root directory of the project, which is used for defining environment variables (such as your database connection)
To connect your database, you need to set the url field of the datasource block in your Prisma schema to your database connection URL:
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}Note that the default schema created by prisma init uses PostgreSQL, so you first need to switch the provider to mysql:
datasource db {
provider = "mysql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}In this case, the url is set via an environment variable which is defined in .env:
DATABASE_URL="mysql://johndoe:randompassword@localhost:3306/mydb"The fields passed to the datasource block are:
-
provider: Specifies themysqldata source connector. -
url: Specifies the connection URL for the MySQL database server. In this case, an environment variable is used to provide the connection URL.
Here's an overview of the components needed for a MySQL connection URL:

You now need to adjust the connection URL to point to your own database.
As an example, for a MySQL database hosted on AWS RDS, the connection URL might look similar to this:
DATABASE_URL="mysql://johndoe:XXX@mysql–instance1.123456789012.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com:3306/mydb"When running MySQL locally, your connection URL typically looks similar to this:
DATABASE_URL="mysql://root:randompassword@localhost:3306/mydb"This is basic information to get started. To continue with your exploration of Prisma, please follow one of the official guides:
- To continue where we left off, proceed to the introspection step.
- To play around with Prisma, go for quickstart guide.
- To start from scratch using MySQL database, use this guide.
- Import and instantiate prisma client
import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client'
const prisma = new PrismaClient()- Retrieve all
Userrecords from the database
// Run inside `async` function
const allUsers = await prisma.user.findMany()- Include the posts relation on each returned
Userobject
// Run inside `async` function
const allUsers = await prisma.user.findMany({
include: { posts: true },
})- Filter all
Postrecords that contain"prisma"
// Run inside `async` function
const filteredPosts = await prisma.post.findMany({
where: {
OR: [
{ title: { contains: 'prisma' } },
{ content: { contains: 'prisma' } },
],
},
})With Prisma Migrate, Prisma's integrated database migration tool, the workflow looks as follows:
- Manually adjust your Prisma data model
- Migrate your development database using the
prisma migrate devCLI command - Use Prisma Client in your application code to access your database

Database migration is the process of migrating data from one or more source databases to one or more target databases by using a database migration service. When a migration is finished, the dataset in the source databases resides fully, though possibly restructured, in the target databases. Clients that accessed the source databases are then switched over to the target databases, and the source databases are turned down.

Database migrations basically track granular changes to your database schema.
ORM:
- What is an ORM, how does it work, and how should I use one?
- What is an ORM - The meaning of Object Relational Mapping Database Tools
Prisma docs:
- What is Prisma?
- Why Prisma?
- Prisma schema
- Set up Prisma guide, when adding to an existing project that has MySQL
- MySQL
Other: