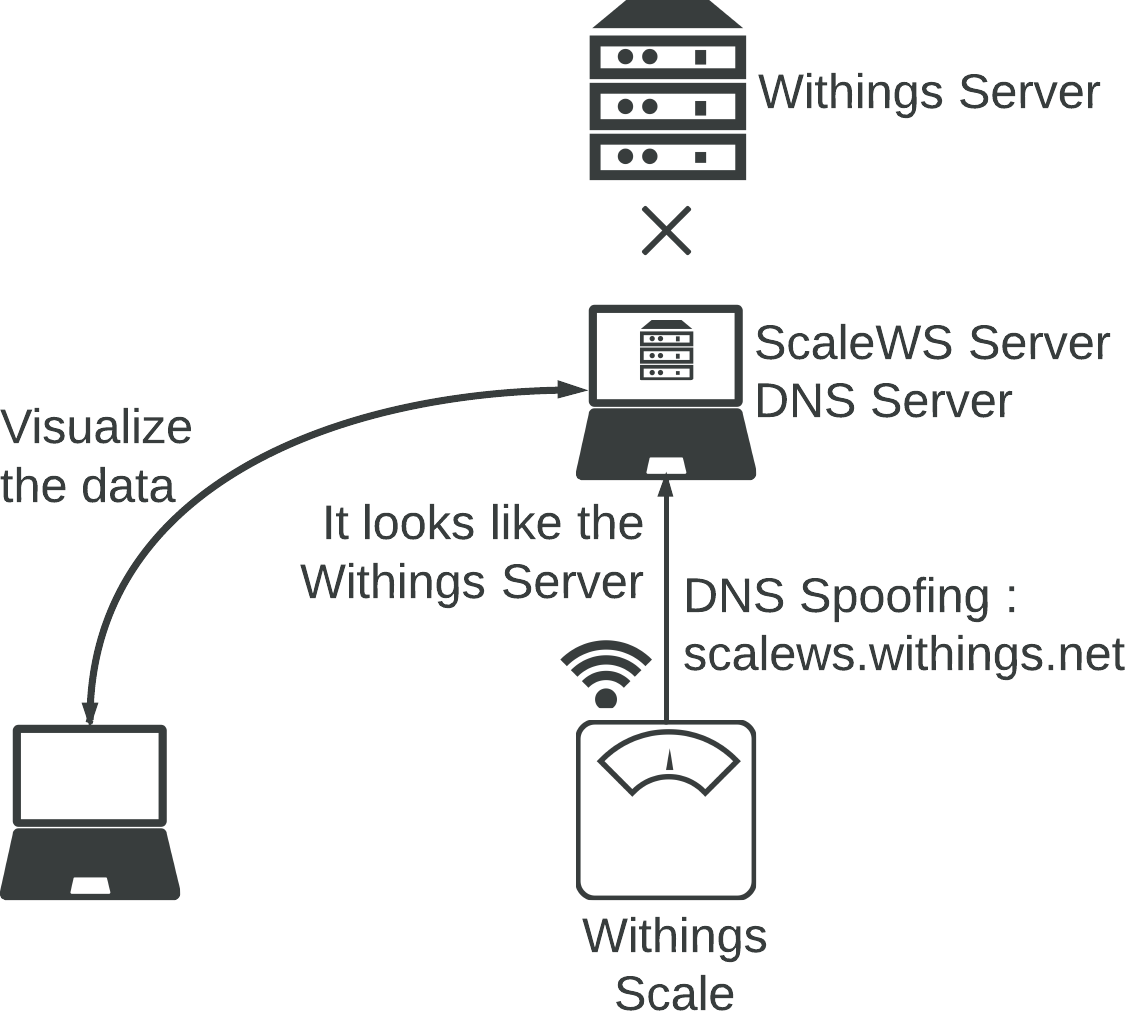
#How to hack the scale First, you need to register the scale to a network/hotspot controlled by you. When the scale is registered, you can configure the DNS Server.
Indeed, in order to hack the scale, you need to redirect the domain scalews.withings.net directly on your server.
This server host the ScaleWS application:
On a GNU/Linux system, you can configure your own DNS-Server with bind9, here is an example.
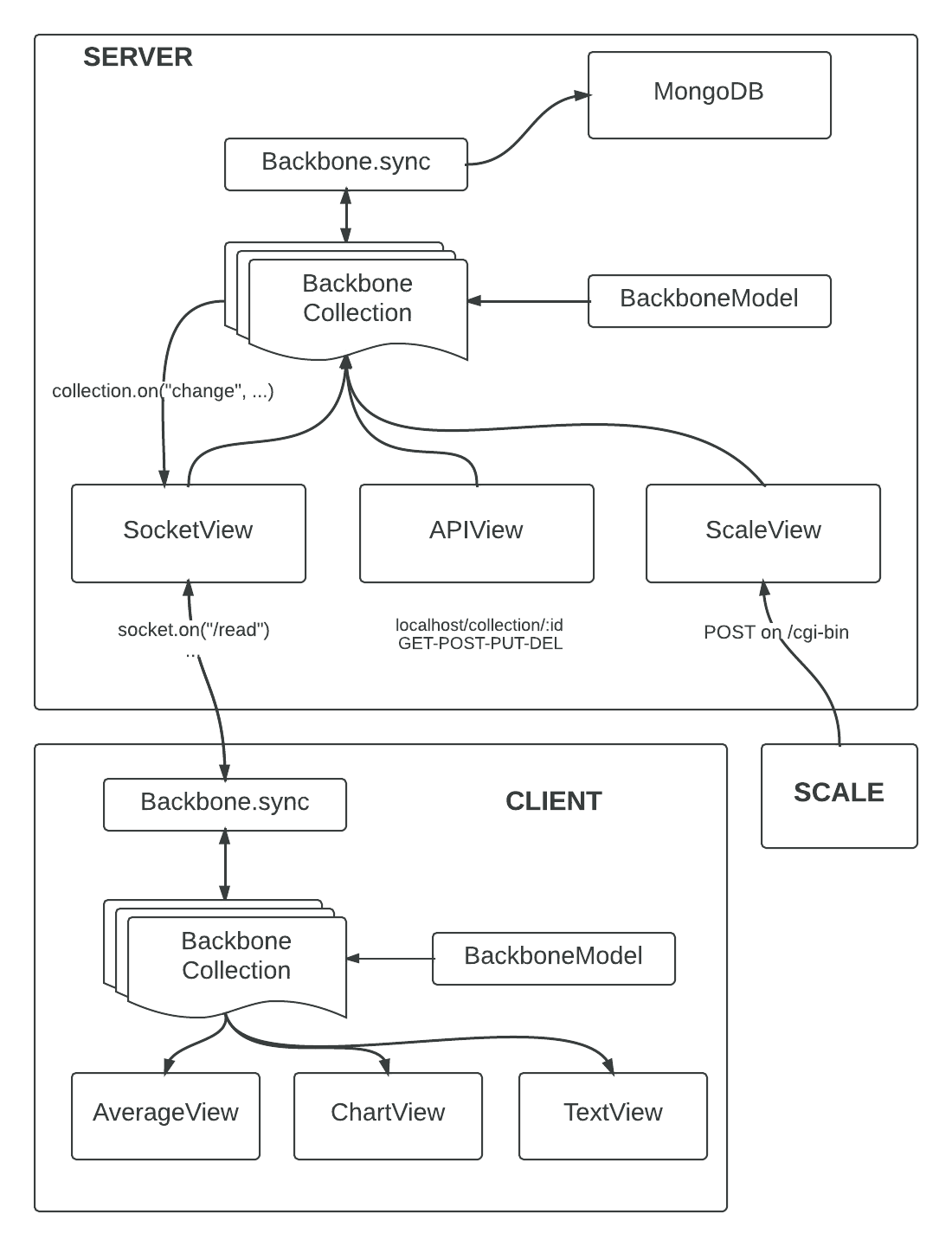
For this application we use a Node.JS Server. It reuses the client's backbone.js collection and model to process data. But in the server case, the collection is sync with a MongoDB database.
When the server starts, it fetches the collection and get the data from the database. When the collection detects new data or any change, it affects the MongoDB database thanks to the overridden function Backbone.sync.
####Configuration
We want to make the code independent from the data in to be able to reuse it for any other sensor.
So we define all specifics things about the scale in a unique file : app/models/Server.Measure.Model.js which adds some methods to the server backbone model.
In this file we define the structure of a measure :
MeasureModel.getSchemaLayout = function(){
return {
value: Number,
type: Number,
date: { type : Date, default : Date.now }
};
};With the same way we define some mask for categories which is reuse by the API :
MeasureModel.getCategoriesMasks = function(){
return {
weight : {type : 1},
heart : {type : 11},
temperature: {type : 12},
fat : {type : 16},
airquality : {type : 35}
};
};The Server Backbone Collection has three different 'Network-Views' :
This one is use by the Scale. It's requested by the scale when there are new data to send.
The scale post the data on with a simple HTTP Post request.
New measures are in JSON. So we just reply to the Scale with the expected JSON message, it is an emulation of the official Withings server :
app.post('/cgi-bin/measure', this.measure.bind(this));
This application provides a simple API REST which give access to the data using JSON. We can Create/Read/Update/Delete data using this API. The action call for the different routes is defined in the app/networkView/apiView.js file.
Here is an example:
app.post(path, _.bind(function(req, res){
httpCallback.call({req : req, res: res},null,this.collection.create(req.body));
}, this));The default path is /{MongoDB CollectionName}/[+ {id || category name}].
You can :
- Add new value : POST on /measure {new model}
- Get values : GET on /measure/[id || category]
- Update a value : PUT on /measure {updated model}
- Delete a value : DEL on /measure/[id] {old model}
This server view is used by our client web application. It is an interface which let you connect on websocket using the socket.io library. So you can do CRUD operations by connecting on the good socket namespace and emit a message. Different socket namespaces are "/read" "/create" "/update" "/delete".
There is another namespace used to push any modification "/main".