This package is just developed to finish my project. So most of scripts are NOT stable enough. By wrapping some functions from other useful packages, it's easy for us to finish our jobs.
This package dependents on some other packages:vcfR,dplyr,genetics,LDheatmap, ...
The dependent packages will be installed at the time you install the package ttplot
#install the ttplot package from Github
if(!require(devtools)) {
install.packages("devtools");
require(devtools)
}
devtools::install_github("YTLogos/ttplot")
Until now there are just several functions
VCF (Variant Call Format) is a text file format. It contains meta-information lines, a header line, and then data lines each containing information about a position in the genome. There is an example how to draw LDheatmap from data in VCF file(plink format). The VCF file looks like:
#This is a test vcf file (test.vcf)
##fileformat=VCFv4.3
##fileDate=20090805
##source=myImputationProgramV3.1
##reference=file:///seq/references/1000GenomesPilot-NCBI36.fasta
##contig=<ID=20,length=62435964,assembly=B36,md5=f126cdf8a6e0c7f379d618ff66beb2da,species="Homo sapiens",taxonomy=x>
##phasing=partial
##INFO=<ID=NS,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Number of Samples With Data">
##INFO=<ID=DP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Total Depth">
##INFO=<ID=AF,Number=A,Type=Float,Description="Allele Frequency">
##INFO=<ID=AA,Number=1,Type=String,Description="Ancestral Allele">
##INFO=<ID=DB,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="dbSNP membership, build 129">
##INFO=<ID=H2,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="HapMap2 membership">
##FILTER=<ID=q10,Description="Quality below 10">
##FILTER=<ID=s50,Description="Less than 50% of samples have data">
##FORMAT=<ID=GT,Number=1,Type=String,Description="Genotype">
##FORMAT=<ID=GQ,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Genotype Quality">
##FORMAT=<ID=DP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Read Depth">
##FORMAT=<ID=HQ,Number=2,Type=Integer,Description="Haplotype Quality">
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT NA00001 NA00002 NA00003
20 14370 rs6054257 G A 29 PASS NS=3;DP=14;AF=0.5;DB;H2 GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0|0:48:1:51,51 1|0:48:8:51,51 1/1:43:5:.,.
20 17330 . T A 3 q10 NS=3;DP=11;AF=0.017 GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0|0:49:3:58,50 0|1:3:5:65,3 0/0:41:3
20 1110696 rs6040355 A G,T 67 PASS NS=2;DP=10;AF=0.333,0.667;AA=T;DB GT:GQ:DP:HQ 1|2:21:6:23,27 2|1:2:0:18,2 2/2:35:4
20 1230237 . T . 47 PASS NS=3;DP=13;AA=T GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0|0:54:7:56,60 0|0:48:4:51,51 0/0:61:2
20 1234567 microsat1 GTC G,GTCT 50 PASS NS=3;DP=9;AA=G GT:GQ:DP 0/1:35:4 0/2:17:2 1/1:40:3
This kind of VCF is very large, so first we can use plink to recode the VCF file
$ plink --vcf test.vcf --recode vcf-iid --out Test -allow-extra-chr
So the final VCF file we will use looks like:
##fileformat=VCFv4.2
##fileDate=20180905
##source=PLINKv1.90
##contig=<ID=chrC07,length=31087537>
##INFO=<ID=PR,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="Provisional reference allele, may not be based on real reference genome">
##FORMAT=<ID=GT,Number=1,Type=String,Description="Genotype">
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT R4157 R4158
chrC07 31076164 . T G . . PR GT 0/0 0/1
chrC07 31076273 . G A . . PR GT 0/0 0/1
chrC07 31076306 . G T . . PR GT 0/0 0/0
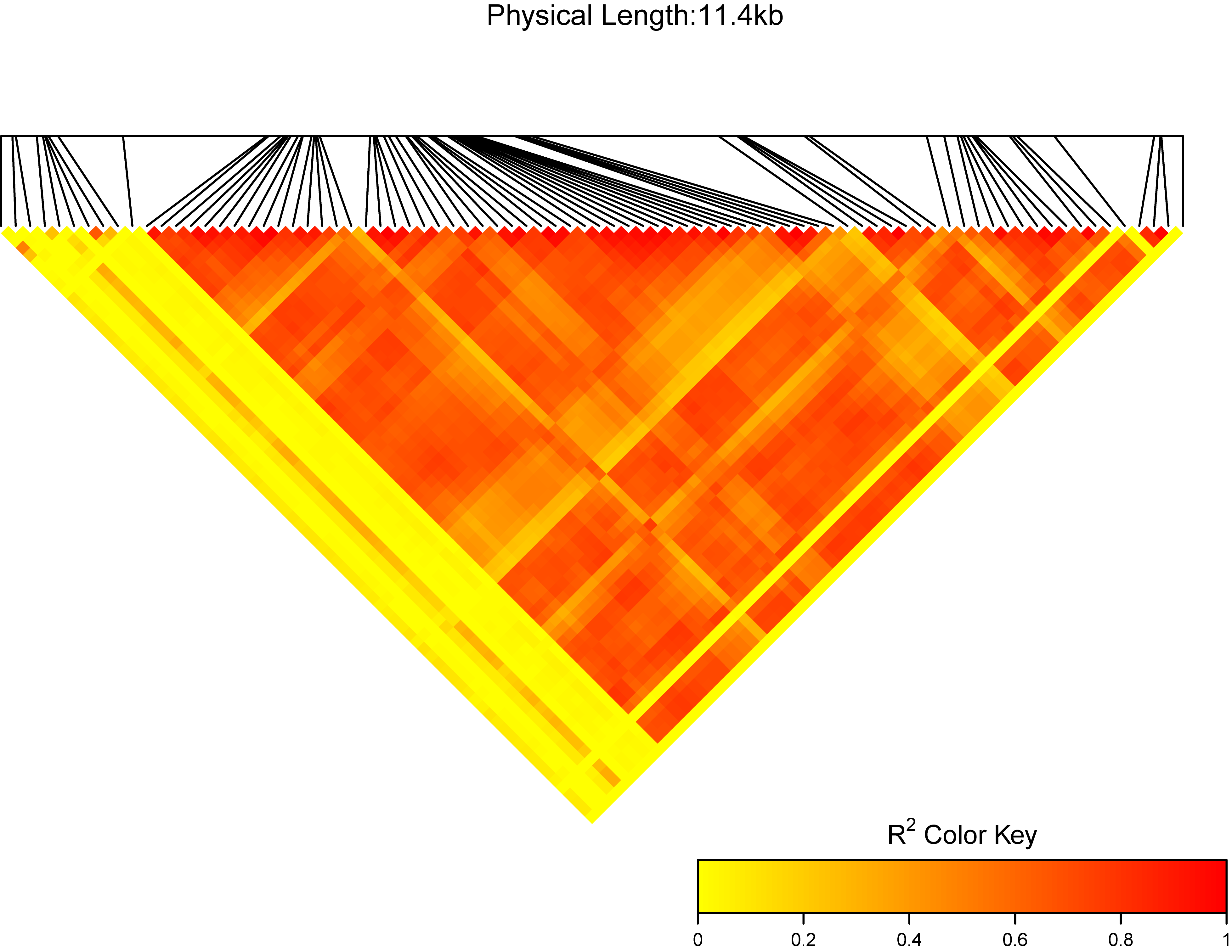
In the extdata directory there is one test file: test.vcf. We can test the function:
library(ttplot)
test <- system.file("extdata", "test.vcf", package = "ttplot")
ttplot::MyLDheatMap(vcffile = test, title = "My gene region")
MyLDheatMap(vcffile, file.output = TRUE, file = "png",
output = "region", title = "region:", verbose = TRUE, dpi = 300)
- vcffile: The plink format vcf file. More detail can see
View(test_vcf). - file.output: a logical, if
file.output=TRUE, the result will be saved. iffile.output=FALSE, the result will be printed. The default isTRUE. - file: a character, users can choose the different output formats of plot, so far, "jpeg", "pdf", "png", "tiff" can be selected by users. The default is "png".
- title: a character, the title of the LDheatmap will be "The LDheatmap of title". the default is "region:". I suggest users use your own title.
- verbose: whether to print the reminder.
- dpi: a number, the picture element for .jpeg, .png and .tiff files. The default is
300.
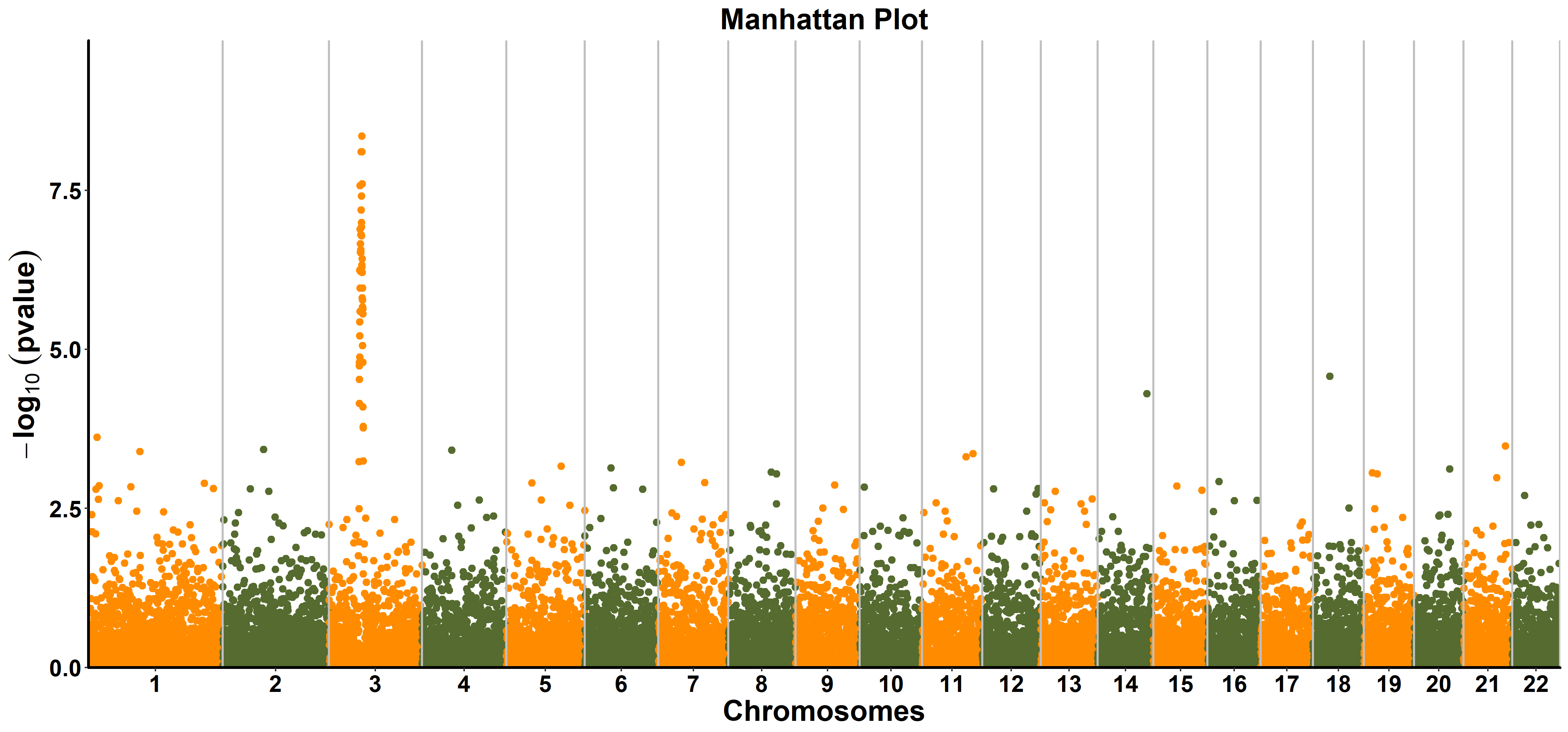
Here, we will use the data gwasResults from R package qqman. This function is provided to make manhattan plot with full ggplot customizability. So next we can customize the manhattan plot with kinds of functions of ggplot2 and add additional layers. The data need be reshaped as following:
> head(gwasResults)
SNP CHR BP P
1 rs1 1 1 0.9148060
2 rs2 1 2 0.9370754
3 rs3 1 3 0.2861395
4 rs4 1 4 0.8304476
5 rs5 1 5 0.6417455
6 rs6 1 6 0.5190959
Then use the function ggmanhattan from ttplot to make a manhattan plot:
ttplot::ggmanhattan(gwasResults)
ggmanhattan(gwasres, snp = NA, bp = NA, chrom = NA, pvalue = NA,
index = NA, file.output = FALSE, file = "png", output = "Trait",
dpi = 300, vlinetype = "solid", vlinesize = 0.75,
title = "Manhattan Plot", color = c("#FF8C00", "#556B2F"),
pointsize = 1.25, verbose = TRUE, ...)
- gwasres a data frame of gwas results.
- snp Name of the column containing
SNPidentifiers; default is 'snp'. - bp Name of the column containing the
SNPpositions; default is'bp'. - chrom Name of the column containing the chromosome identifers; default is
'chrom'. - pvalue Name of the column containing the p values; default is
'pvalue'. - file.output a logical, if file.output=
TRUE, the result will be saved. if file.output=FALSE, the result will be printed. The default isTRUE. - file a character, users can choose the different output formats of plot, so far,
"jpeg","pdf","png","tiff"can be selected by users. The default is"png". - dpi a number, the picture element for .jpeg, .png and .tiff files. The default is 300.
- vlinetype the type of vline (
geom_vline()). The default is"solid". - vlinesize the size of the vline. The default is 0.75.
- title the title of manhattan plot. The default is
"Manhattan Plot". - color the colors of alternate chromosome. The default is c(
"#FF8C00","#556B2F"). - pointsize the size of point. The default is 1.25.
This function need two input files: gff, snp.
library(ttplot)
gff <- read.table(system.file("extdata", "test.gff", package = "ttplot"), header= TRUE)
head(gff)
chr start end gene
1 436789 437474 chrA01g000077
1 439907 442623 chrA01g000078
1 448692 449999 chrA01g000079
1 454920 456931 chrA01g000080
1 457568 460619 chrA01g000081
1 461129 462693 chrA01g000082
snp <- read.table(system.file("extdata", "test_sig_snp.txt", package = "ttplot"), header= TRUE)
head(snp)
SNP CHR BP P
1_500000 1 500000 5.53e-11
1_650000 1 650000 7.04e-09
2_1880000 2 1880000 3.84e-09
3_30500000 3 30500000 7.57e-08
Then we can get the candidate genes in regions based on significant SNPs of GWAS results.
ttplot::get_gene_from_snp(gff = gff, sig.snp = snp, distance = 20000, file.save = FALSE)
The distance you choose is 20000bp!
You have 4 significant SNPs and 130 genes!
Now we will extract the genes in the significant regions! This will need some time, please wait for severals minutes! ...
The result is :
-------------------------------------------------------------
# A tibble: 9 x 5
chrom geneid gene_start gene_end snp_location
<dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 chrA01g000088 479923 485997 500000
1 chrA01g000089 495531 497917 500000
1 chrA01g000090 498488 499689 500000
1 chrA01g000091 499749 501301 500000
1 chrA01g000092 503622 507079 500000
1 chrA01g000093 507659 510321 500000
1 chrA01g000094 515103 516863 500000
1 chrA01g000095 517335 518776 500000
1 chrA01g000096 519020 520668 500000
Usage
get_gene_from_snp(gff, sig.snp, distance = 50000, file.save = TRUE,
file.type = "csv", gff.chrom = NA, snp.chrom = NA, geneid = NA,
pvalue = NA, gene_start = NA, gene_end = NA, snp_location = NA,
verbose = TRUE, ...)
- gff: a data frame of all the gene (transcript), must have column names.
- sig.snp: a data frame of significant SNPs.
- distance: numeric (bp), it is to define the region. The default is 50000, you need to choose it based on the LD distance in your study.
- file.save: a logical, if file.output=TRUE, the result will be saved. if file.output=FALSE, the result will be printed. The default is TRUE.
- file.type: a character, users can choose the different output formats, so far, "csv", "txt", "xlsx" can be selected by users. The default is "csv".
- gff.chrom: Name of the column containing the chromosome identifers in the gff file; default is NA.
- snp.chrom: Name of the column containing the chromosome identifers in the snp.sig file; default is NA.
- geneid: Name of the column containing the geneid in gff file; default is NA.
- pvalue: Name of the column containing the p values in snp.sig file; default is NA.
- snp_location: Name of the column containing the snp position in snp.sig file; default is NA.