解释该问题,需要了解以下的知识点:Agent工具 -> FunctionCall - ToolCall
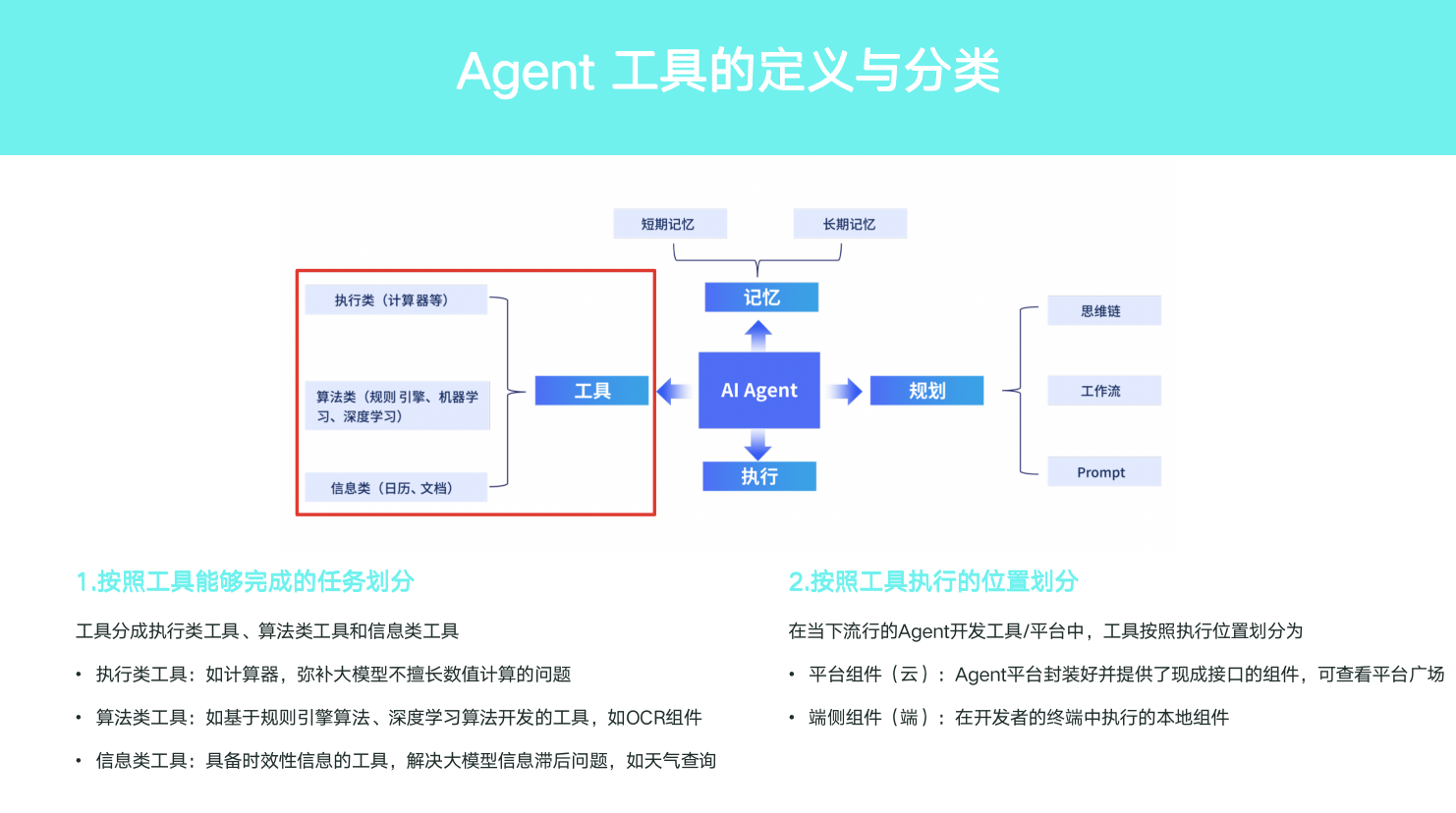
AIAgent 有四大核心组件:记忆、规划、工具和执行。其中工具部分,与我们的开发关系最密切,在各类Agent开发平台/工具中,常被称为“组件”、"插件"、"能力"等.
关于Agent的工具的定义与分类,如下图~
Agent使用工具的流程,一般称为FunctionCall,最早由OpenAI提出,并在Assistant API中广泛应用。
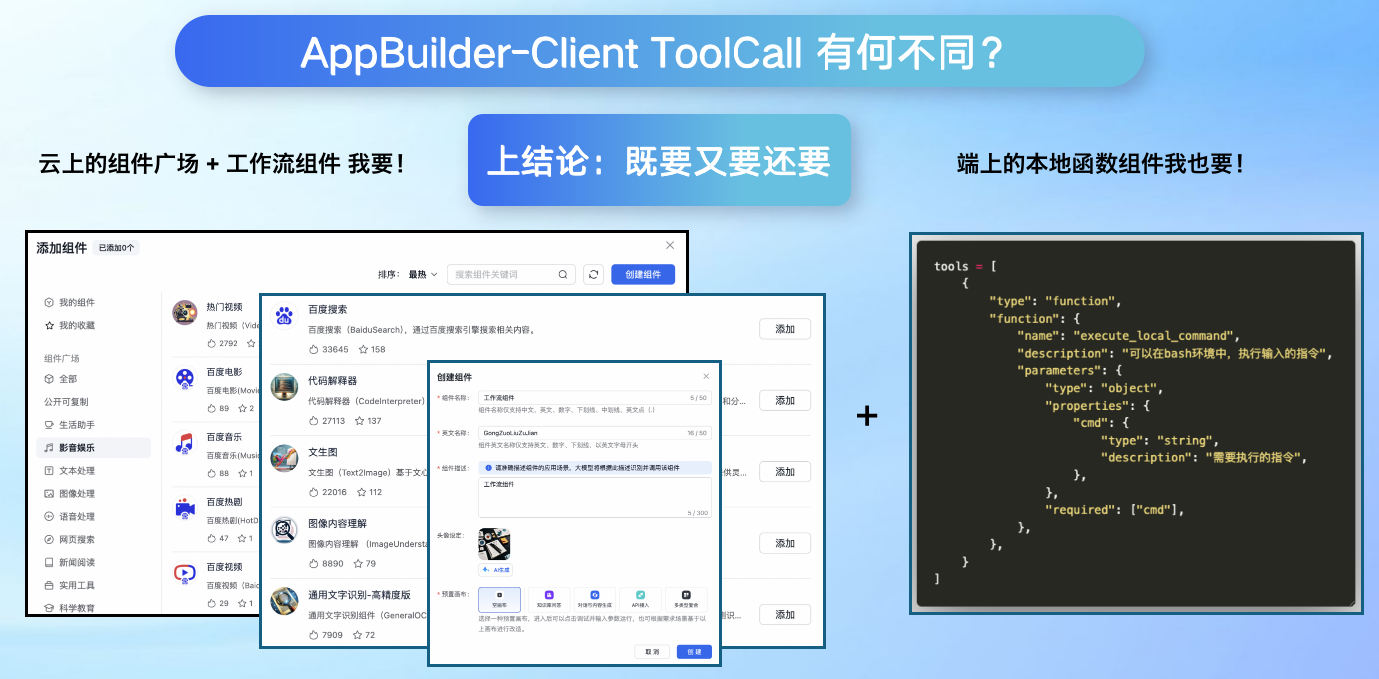
ToolCall,则是AppBuilder平台提出的一种进阶的FunctionCall,本质与OpenAI的FunctionCall一致,但具有以下两个特点:
-
端云组件联动: Agent 调用工具时,可以同时调用云端和本地组件。
-
组件类型泛化: AppBuilder在未来会支持多种类型组件,已经超出了Function的含义,例如数据库、记忆库、工作流等等
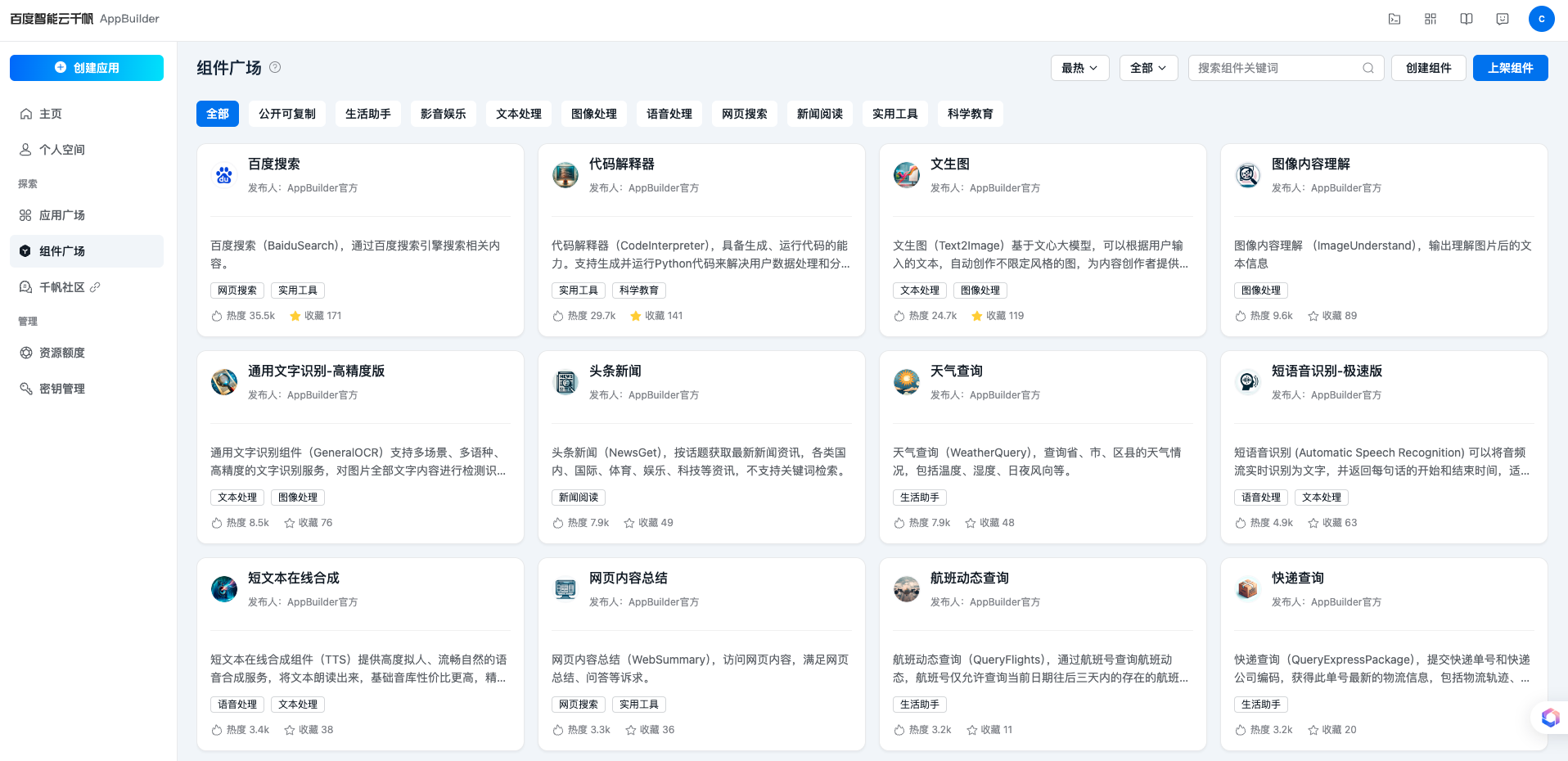
我们首先从工具的执行位置出发展开~ 在使用如AppBuilder / Coze 等平台开发Agent时,我们可以使用很多平台组件广场中,官方提供的组件,这里组件开箱即用,非常方便。
但是存在一个问题,基于平台云端组件开发的应用,无法调用内网/局域网/私域的知识与能力,也无法与本地的工具进行联动,限制了Agent的灵活性。
我们在解决实际业务问题时,常遇到需要访问内网链接API或本地/硬件功能的FunctionCall需求,AppBuilder ToolCall可以解决这个问题:
- 1、用户可注册一个本地运行的组件到已发布的应用
- 2、由AppBuilder-Agent的云端思考模型进行规划和参数生成
- 3、用户基于生成的参数调用本地组件,并再上传运行结果
- 4、以此实现将本地组件能力嵌入到应用整体流程
我们可以将Agent的黑箱拆解为以下几个部分:
- Agent的背景信息
- Agent的输入信息
- Agent的思考过程
- Agent触发组件调用
- Agent基于组件输出反思总结
- 角色定义描述(Prompt):定义Agent的角色
- 能力描述(Prompt):定义Agent可以干什么
- 工具描述(JsonSchema/Str):将工具的输入和输出,按照规范,定义为一段字符串,作为最终大模型Prompt的一部分
- 用户输入(Query/Prompt):用户输入的文本
- 对话相关的文件(File/Url):与本地对话相关的文件路径
AppBuilder-Agent会将背景信息与输入信息,拼接为最终的Prompt,然后调用大模型推理。
Prompt的一个简单且直观的例子是:
你是{角色定义描述},你可以做以下事情:{能力描述},你可以使用这些工具:{工具描述-description},工具依赖的输入是:{工具描述-paramters-properties-name},这些输入的格式分别是{工具描述-paramters-properties-type}。现在用户的问题是{用户输入},与该问题相关的文件是{对话相关的文件},请你解决用户的这个问题。
如果用户的query和组件能够解决的问题匹配,那么大模型就会尝试根据prompt里给出的工具的描述,从query中提炼出该次调用工具所需的参数,生成一个ToolCall命令,交给执行组件的模块去执行。
例如,我们给出的组件能力是"查找公司内指定人员的信息",函数的参数名为"name"。当用户输入"查找张三的信息",大模型会从query中提炼出参数"name=张三"这个信息。
组件运行模块执行组件后,会给出字符串形式的结果给到Agent,Agent会再次将结果拼接为Prompt,然后调用大模型推理。判断用户的需求是否已经解决。如果解决了,则经过一个对话模块,总结用户的需求,并生成一个对话记录。如果未解决,则继续调用大模型推理,尝试调用更多的工具,直到用户的需求被解决。
我们以AppBuilder-SDK中的AppBuilder-Client的基础代码为例,介绍开发者应该如何使用ToolCall功能
import appbuilder
# 实例化AppBuilderClient
app_client = appbuilder.AppBuilderClient(app_id)
conversation_id = app_client.create_conversation()
# 第一次对话,输入原始的query 和 工具描述
message_1 = app_client.run(
conversation_id=conversation_id,
query="请问张三同学的生日是哪天?",
tools=tools
)
tool_call = message_1.content.events[-1].tool_calls[-1]
tool_call_id = tool_call.id
# 第二次对话,在本地执行组件后,上传组件的运行结果
tool_call_result = "张三同学的生日是2008年8月8日"
message_2 = app_client.run(
conversation_id=conversation_id,
tool_outputs=[{
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"output": tool_call_result
}]
)
print(message_2.content)其中AppBuilderClient的run方法是核心,我们展开该函数的定义和参数介绍:
AppBuilderClient().run() -> Message
def run(self, conversation_id: str,
query: str = "",
file_ids: list = [],
stream: bool = False,
tools: list[data_class.Tool] = None,
tool_outputs: list[data_class.ToolOutput] = None,
**kwargs
) -> Message:
r"""
参数:
query (str: 必须): query内容
conversation_id (str, 必须): 唯一会话ID,如需开始新的会话,请使用self.create_conversation创建新的会话
file_ids(list[str], 可选):
stream (bool, 可选): 为True时,流式返回,需要将message.content.answer拼接起来才是完整的回答;为False时,对应非流式返回
tools(list[data_class.Tools], 可选): 一个Tools组成的列表,其中每个Tools对应一个工具的配置, 默认为None
tool_outputs(list[data_class.ToolOutput], 可选): 工具输出列表,格式为list[ToolOutput], ToolOutputd内容为本地的工具执行结果,以自然语言/json dump str描述,默认为None
返回: message (obj: `Message`): 对话结果.
"""
pass| 参数名称 | 参数类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 | 示例值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| conversation_id | String | 是 | 会话ID | |
| query | String | 否 | query问题内容 | "今天天气怎么样?" |
| file_ids | list[String] | 否 | 对话可引用的文档ID | |
| stream | Bool | 否 | 为true时则流式返回,为false时则一次性返回所有内容, 推荐设为true,降低首token时延 | False |
| tools | List[Tool] | 否 | 一个列表,其中每个字典对应一个工具的配置 | |
| tools[0] | Tool | 否 | 工具配置 | |
| +type | String | 否 | 枚举: file_retrieval: 知识库检索工具能够理解文档内容,支持用户针对文档内容的问答。 code_interpreter: 代码解释器, 代码解释器能够生成并执行代码,从而协助用户解决复杂问题,涵盖科学计算(包括普通数学计算题)、数据可视化、文件编辑处理(图片、PDF文档、视频、音频等)、文件格式转换(如WAV、MP3、text、SRT、PNG、jpg、MP4、GIF、MP3等)、数据分析&清洗&处理(文件以excel、csv格式为主)、机器学习&深度学习建模&自然语言处理等多个领域。 function: 支持fucntion call模式调用工具 |
|
| +function | Function | 否 | Function工具描述 仅当type为 **function** 时需要且必须填写 |
|
| ++name | String | 否 | 函数名 只允许数字、大小写字母和中划线和下划线,最大长度为64个字符。一次运行中唯一。 |
|
| ++description | String | 否 | 工具描述 | |
| ++parameters | Dict | 否 | 工具参数, json_schema格式 | |
| tool_outputs | List[ToolOutput] | 否 | 内容为本地的工具执行结果,以自然语言/json dump str描述 | |
| tool_outputs[0] | ToolOutput | 否 | 工具执行结果 | |
| +tool_call_id | String | 否 | 工具调用ID | |
| +output | String | 否 | 工具输出 |
Tool与Function是本地组件的描述,类型为object,其定义如下:
class Tool(BaseModel):
type: str = "function"
function: Function = Field(..., description="工具信息")
class Function(BaseModel):
name: str = Field(..., description="工具名称")
description: str = Field(..., description="工具描述")
parameters: dict = Field(..., description="工具参数, json_schema格式")ToolOutput是本地组件的执行结果,需要再次上传到Agent,参与思考,类型为object,其定义如下:
class ToolOutput(BaseModel):
tool_call_id: str = Field(..., description="工具调用ID")
output: str = Field(..., description="工具输出")以下示例展示了三种方式来使用 ToolCall 进行调用,并演示了如何在 AppBuilder 环境中配置和执行会话调用。
方式1:使用 JSONSchema 格式直接描述 tools 调用
import appbuilder
from appbuilder.core.console.appbuilder_client import data_class
import os
# 请前往千帆AppBuilder官网创建密钥,流程详见:https://cloud.baidu.com/doc/AppBuilder/s/Olq6grrt6#1%E3%80%81%E5%88%9B%E5%BB%BA%E5%AF%86%E9%92%A5
# 设置环境变量
os.environ["APPBUILDER_TOKEN"] = "..."
app_id = "..." # 已发布AppBuilder应用的ID
# 初始化智能体
client = appbuilder.AppBuilderClient(app_id)
# 创建会话
conversation_id = client.create_conversation()
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "仅支持中国城市的天气查询,参数location为中国城市名称,其他国家城市不支持天气查询",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名,举例:北京",
},
"unit": {"type": "string", "enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]},
},
"required": ["location", "unit"],
},
},
}
]
msg = client.run(
conversation_id=conversation_id, query="今天北京天气怎么样?", tools=tools
)
print(msg.model_dump_json(indent=4))
event = msg.content.events[-1]
msg_2 = client.run(
conversation_id=conversation_id,
tool_outputs=[{"tool_call_id": event.tool_calls[-1].id, "output": "北京今天35度"}],
)
print(msg_2.model_dump_json(indent=4))方式2: 使用 function_to_model 将函数对象传递为 ToolCall 的调用
import appbuilder
import os
# 请前往千帆AppBuilder官网创建密钥,流程详见:https://cloud.baidu.com/doc/AppBuilder/s/Olq6grrt6#1%E3%80%81%E5%88%9B%E5%BB%BA%E5%AF%86%E9%92%A5
# 设置环境变量
os.environ["APPBUILDER_TOKEN"] = "..."
app_id = "..." # 已发布AppBuilder应用的ID
# 初始化智能体
client = appbuilder.AppBuilderClient(app_id)
# 创建会话
conversation_id = client.create_conversation()
#注意:要使用此方法要为函数写好注释。最好按照谷歌规范来写
#定义示例函数
def get_current_weather(location: str, unit: str) -> str:
"""获取指定中国城市的当前天气信息。
仅支持中国城市的天气查询。参数 `location` 为中国城市名称,其他国家城市不支持天气查询。
Args:
location (str): 城市名,例如:"北京"。
unit (int): 温度单位,支持 "celsius" 或 "fahrenheit"。
Returns:
str: 天气情况描述
"""
return "北京今天25度"
#定义函数列表
functions = [get_current_weather]
function_map = {f.__name__: f for f in functions}
#调用大模型
msg = client.run(
conversation_id=conversation_id,
query="今天北京的天气怎么样?",
tools = [appbuilder.Manifest.from_function(f) for f in functions]
)
print(msg.model_dump_json(indent=4))
# 获取最后的事件和工具调用信息
event = msg.content.events[-1]
tool_call = event.tool_calls[-1]
# 获取函数名称和参数
name = tool_call.function.name
args = tool_call.function.arguments
# 将函数名称映射到具体的函数并执行
raw_result = function_map[name](**args)
# 传递工具的输出
msg_2 = client.run(
conversation_id=conversation_id,
tool_outputs=[{
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"output": str(raw_result)
}],
)
print(msg_2.model_dump_json(indent=4))方式3: 使用装饰器进行描述
import os
import json
import appbuilder
from appbuilder import manifest, manifest_parameter
# 请前往千帆AppBuilder官网创建密钥,流程详见:https://cloud.baidu.com/doc/AppBuilder/s/Olq6grrt6#1%E3%80%81%E5%88%9B%E5%BB%BA%E5%AF%86%E9%92%A5
# 设置环境变量
os.environ["APPBUILDER_TOKEN"] = ""
app_id = "" # 已发布AppBuilder应用的ID
# 初始化智能体
client = appbuilder.AppBuilderClient(app_id)
# 创建会话
conversation_id = client.create_conversation()
#使用manifest装饰描述函数,manifest_parameter装饰器描述参数,manifest_return装饰器描述函数返回值。
@manifest(description="获取指定中国城市的当前天气信息。仅支持中国城市的天气查询。参数 `location` 为中国城市名称,其他国家城市不支持天气查询。")
@manifest_parameter(name="location", description="城市名,例如:北京。")
@manifest_parameter(name="unit", description="温度单位,支持 'celsius' 或 'fahrenheit'")
#定义示例函数
def get_current_weather(location: str, unit: str) -> str:
return "北京今天25度"
print(json.dumps(appbuilder.Manifest.from_function(get_current_weather), indent=4, ensure_ascii=False))
#定义函数列表
functions = [get_current_weather]
function_map = {f.__name__: f for f in functions}
#调用大模型
msg = client.run(
conversation_id=conversation_id,
query="今天北京的天气怎么样?",
tools = [appbuilder.Manifest.from_function(f) for f in functions]
)
print(msg.model_dump_json(indent=4))
# 获取最后的事件和工具调用信息
event = msg.content.events[-1]
tool_call = event.tool_calls[-1]
# 获取函数名称和参数
name = tool_call.function.name
args = tool_call.function.arguments
# 将函数名称映射到具体的函数并执行
raw_result = function_map[name](**args)
# 传递工具的输出
msg_2 = client.run(
conversation_id=conversation_id,
tool_outputs=[{
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"output": str(raw_result)
}],
)
print(msg_2.model_dump_json(indent=4))创建tool的json文件
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_cur_whether",
"description": "这是一个获得指定地点天气的工具",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "省,市名,例如:河北省"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": [
"摄氏度",
"华氏度"
]
}
},
"required": [
"location"
]
}
}
}package org.example;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName;
import com.baidubce.appbuilder.base.exception.AppBuilderServerException;
import com.baidubce.appbuilder.console.appbuilderclient.AppBuilderClient;
import com.baidubce.appbuilder.model.appbuilderclient.AppBuilderClientIterator;
import com.baidubce.appbuilder.model.appbuilderclient.AppBuilderClientResult;
import com.baidubce.appbuilder.model.appbuilderclient.Event;
import com.baidubce.appbuilder.base.utils.json.JsonUtils;
class AppBuilderClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, AppBuilderServerException {
System.setProperty("APPBUILDER_TOKEN", "请设置正确的应用密钥");
String appId = "请设置正确的应用ID";
AppBuilderClient builder = new AppBuilderClient(appId);
String conversationId = builder.createConversation();
AppBuilderClientRunRequest request = new AppBuilderClientRunRequest(appId, conversationId, "今天北京的天气怎么样?", false);
String toolJson = new String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("json文件所在的路径")));
request.setTools(toolJson);
AppBuilderClientIterator itor = builder.run(request);
String ToolCallID = "";
while (itor.hasNext()) {
AppBuilderClientResult result = itor.next();
Event lastEvent = result.getEvents()[result.getEvents().length - 1];
ToolCallID = lastEvent.getToolCalls()[lastEvent.getToolCalls().length - 1].getId();
System.out.println(result);
}
AppBuilderClientRunRequest request2 = new AppBuilderClientRunRequest(appId, conversationId);
request2.setToolOutputs(ToolCallID, "北京今天35度");
AppBuilderClientIterator itor2 = builder.run(request2);
while (itor2.hasNext()) {
AppBuilderClientResult result = itor2.next();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}package main
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
"github.com/baidubce/app-builder/go/appbuilder"
)
func main() {
// 设置APPBUILDER_TOKEN、GATEWAY_URL_V2环境变量
os.Setenv("APPBUILDER_TOKEN", "请设置正确的应用密钥")
// 默认可不填,默认值是 https://qianfan.baidubce.com
os.Setenv("GATEWAY_URL_V2", "")
config, err := appbuilder.NewSDKConfig("", "")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("new config failed: ", err)
return
}
// 初始化实例
appID := "请填写正确的应用ID"
builder, err := appbuilder.NewAppBuilderClient(appID, config)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("new agent builder failed: ", err)
return
}
// 创建对话ID
conversationID, err := builder.CreateConversation()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("create conversation failed: ", err)
return
}
jsonStr := `
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_cur_whether",
"description": "这是一个获得指定地点天气的工具",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "省,市名,例如:河北省"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["摄氏度", "华氏度"]
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
}`
var tool Tool
err = json.Unmarshal([]byte(jsonStr), &tool)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("unmarshal tool error:", err)
return
}
i, err := client.Run(appbuilder.AppBuilderClientRunRequest{
AppID: appID,
Query: "今天北京的天气怎么样?",
ConversationID: conversationID,
Stream: true,
Tools: []appbuilder.Tool{tool},
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("run failed:", err)
}
totalAnswer := ""
toolCallID := ""
for answer, err := i.Next(); err == nil; answer, err = i.Next() {
totalAnswer += answer.Answer
lastEvent := answer.Events[len(answer.Events)-1]
toolCallID = lastEvent.ToolCalls[len(lastEvent.ToolCalls)-1].ID
}
i2, err := client.Run(appbuilder.AppBuilderClientRunRequest{
ConversationID: conversationID,
AppID: appID,
ToolOutputs: []appbuilder.ToolOutput{
{
ToolCallID: toolCallID,
Output: "北京今天35度",
},
},
Stream: true,
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("run failed: ", err)
}
for answer, err := i2.Next(); err == nil; answer, err = i2.Next() {
totalAnswer = totalAnswer + answer.Answer
for _, ev := range answer.Events {
evJSON, _ := json.Marshal(ev)
fmt.Println(string(evJSON))
}
}
fmt.Println("----------------answer-------------------")
fmt.Println(totalAnswer)
}-
注意:当前功能为试运行阶段,可能存在如下问题,如使用过程遇到其他问题,欢迎提issue或微信群讨论。
-
需开启"组件/知识库结论可直接作为回复"
-
组件名称不是界面上的原始名字,而是个人空间组件列表中的英文名
-
自定义组件的参数不能使用系统参数,可以使用用户添加的参数
-
部分官方组件使用的参数与界面上的参数不一致
-
package main
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
"github.com/baidubce/app-builder/go/appbuilder"
)
func main() {
// 设置APPBUILDER_TOKEN、GATEWAY_URL_V2环境变量
os.Setenv("APPBUILDER_TOKEN", "请设置正确的应用密钥")
// 默认可不填,默认值是 https://qianfan.baidubce.com
os.Setenv("GATEWAY_URL_V2", "")
config, err := appbuilder.NewSDKConfig("", "")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("new config failed: ", err)
return
}
// 初始化实例
appID := "请填写正确的应用ID"
builder, err := appbuilder.NewAppBuilderClient(appID, config)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("new agent builder failed: ", err)
return
}
// 创建对话ID
conversationID, err := builder.CreateConversation()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("create conversation failed: ", err)
return
}
// 注意使用创建应用中用到的组件。名称、参数均以实际使用的组件为准。
input := make(map[string]any)
input["city"] = "北京"
end_user_id := "go_toolchoice_demo"
i, err := client.Run(AppBuilderClientRunRequest{
ConversationID: conversationID,
AppID: appID,
Query: "",
EndUserID: &end_user_id,
Stream: false,
ToolChoice: &ToolChoice{
Type: "function",
Function: ToolChoiceFunction{
Name: "WeatherQuery",
Input: input,
},
},
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("run failed: ", err)
return
}
for answer, err := i.Next(); err == nil; answer, err = i.Next() {
for _, ev := range answer.Events {
evJSON, _ := json.Marshal(ev)
fmt.Println(string(evJSON))
}
}
}