如果阅读时,发现错误,或者动画不可以显示的问题可以添加我微信好友 tan45du_one ,备注 github + 题目 + 问题 向我反馈
感谢支持,该仓库会一直维护,希望对各位有一丢丢帮助。
另外希望手机阅读的同学可以来我的 公众号:程序厨 两个平台同步,想要和题友一起刷题,互相监督的同学,可以在我的小屋点击刷题小队进入。
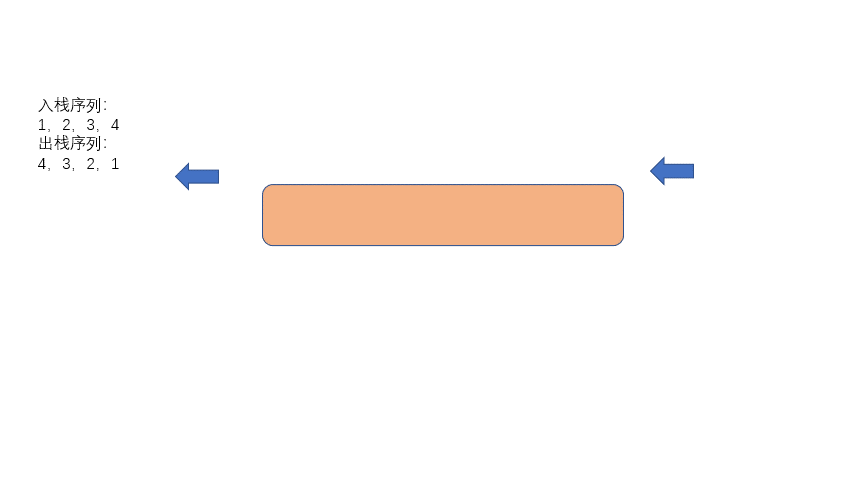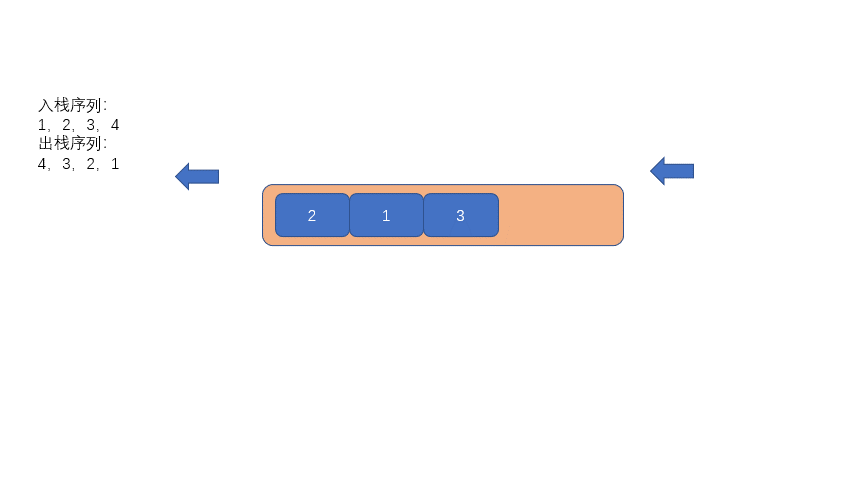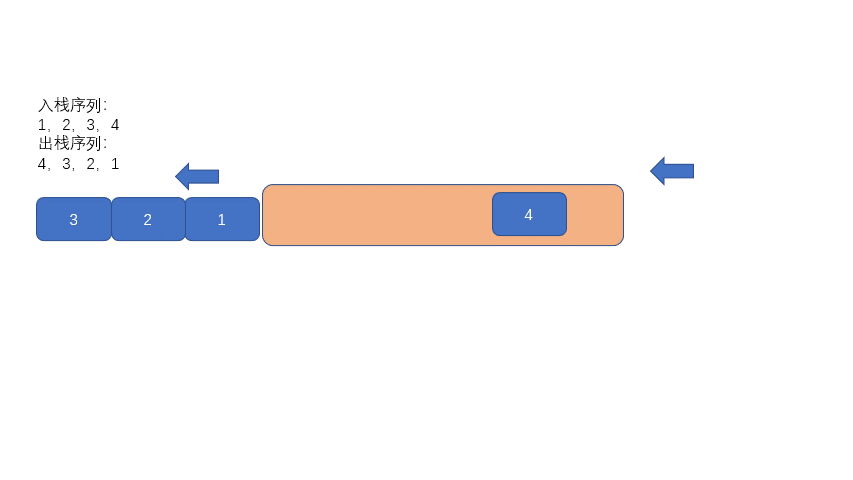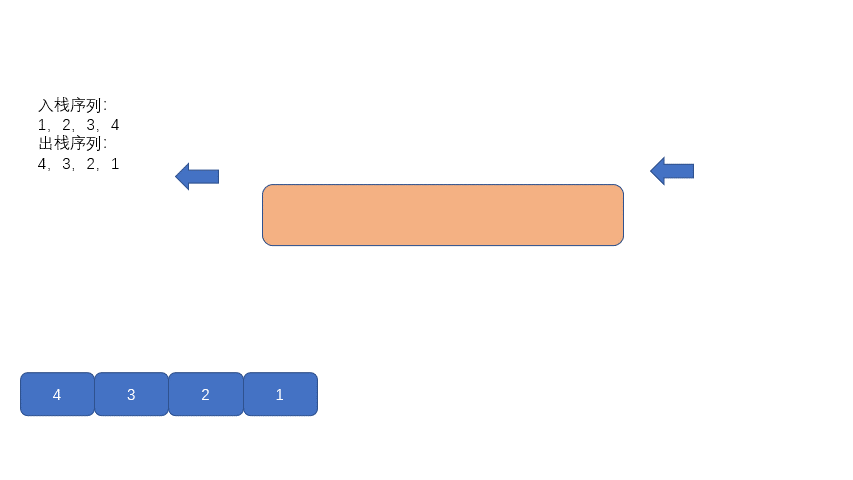
我们昨天实现了如何用两个栈实现队列,原理很简单,今天我们来实现一下如何用队列实现栈。
其实原理也很简单,我们利用队列先进先出的特点,每次队列模拟入栈时,我们先将队列之前入队的元素都出列,仅保留最后一个进队的元素。
然后再重新入队,这样就实现了颠倒队列中的元素。比如我们首先入队 1,然后再入队 2,我们需要将元素 1 出队,然后再重新入队,则实现了队列内元素序列变成了 2,1。
废话不多说,我们继续看动图
下面我们来看一下题目代码,也是很容易理解。
Java Code:
class MyStack {
//初始化队列
Queue<Integer> queue;
public MyStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
}
//模拟入栈操作
public void push(int x) {
queue.offer(x);
//将之前的全部都出队,然后再入队
for(int i = 1;i<queue.size();i++){
queue.offer(queue.poll());
}
}
//模拟出栈
public int pop() {
return queue.poll();
}
//返回栈顶元素
public int top() {
return queue.peek();
}
//判断是否为空
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}JS Code:
var MyStack = function () {
this.queue = [];
};
MyStack.prototype.push = function (x) {
this.queue.push(x);
if (this.queue.length > 1) {
let i = this.queue.length - 1;
while (i) {
this.queue.push(this.queue.shift());
i--;
}
}
};
MyStack.prototype.pop = function () {
return this.queue.shift();
};
MyStack.prototype.top = function () {
return this.empty() ? null : this.queue[0];
};
MyStack.prototype.empty = function () {
return !this.queue.length;
};C++ Code:
class MyStack {
queue <int> q;
public:
void push(int x) {
q.push(x);
for(int i = 1;i < q.size();i++){
int val = q.front();
q.push(val);
q.pop();
}
}
int pop() {
int val = q.front();
q.pop();
return val;
}
int top() {
return q.front();
}
bool empty() {
return q.empty();
}
};