const rules = {
option1: { rule1: "value1", rule2: "value2" },
option2: { rule1: "value3", rule2: "value4" },
option3: { rule1: "value5", rule2: "value6" }
};Example 1
const rules = {
rock: { beats: "scissors", losesTo: "paper" },
paper: { beats: "rock", losesTo: "scissors" },
scissors: { beats: "paper", losesTo: "rock" }
};Example 2
const rules = {
name: { required: true, maxLength: 50 },
email: { required: true, emailFormat: true },
age: { required: true, minValue: 18, maxValue: 100 },
password: { required: true, minLength: 8, hasNumber: true, hasSpecialChar: true }
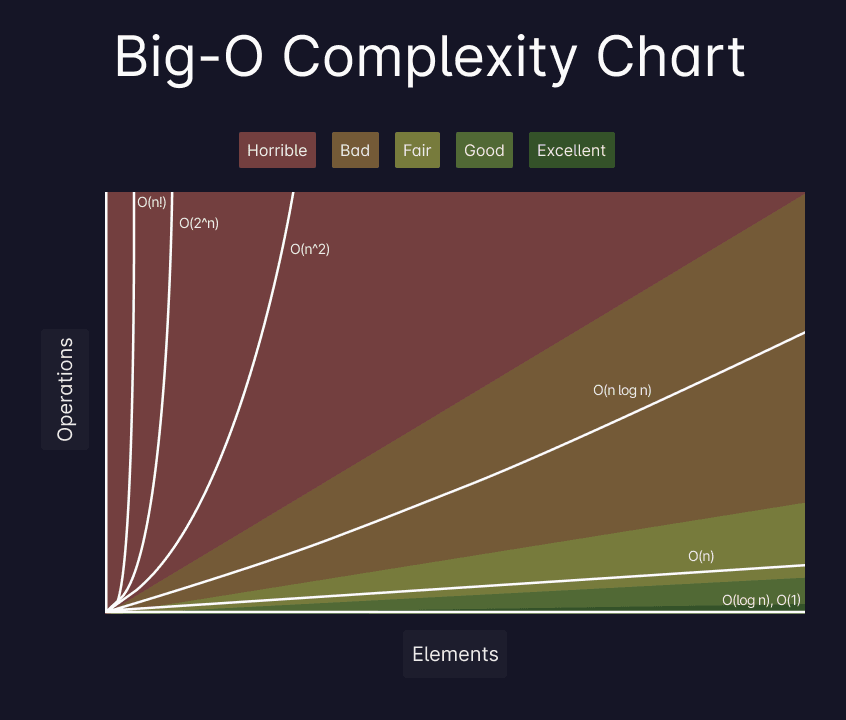
};Big-O notation, represents an algorithm's worst-case complexity. It uses algebraic terms to describe the complexity of an algorithm, allowing you to measure its efficiency and performance.
Different data structures have different time complexities for the same operations. Below you can find average and worst time complexities for data structures used commonly in web development.
| Data Structure | Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion |
|---------------------|----------|----------|-----------|-----------|
| Array | Θ(1) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) |
| Queue | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) |
| Stack | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) |
| Linked List | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) |
| Doubly Linked List | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) |
| Skip List | Θ(log n) | Θ(log n) | Θ(log n) | Θ(log n) |
| Hash Table | N/A | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) |
| Binary Search Tree | Θ(log n) | Θ(log n) | Θ(log n) | Θ(log n) || Data Structure | Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion |
|--------------------|--------|--------|-----------|----------|
| Array | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Queue | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Stack | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Linked List | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Doubly Linked List | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Skip List | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Hash Table | N/A | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Binary Search Tree | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |Similar to data structures, different array sorting algorithms have different time complexities. Below you can find the best, average and worst time complexities for the most common array sorting algorithms.
| Algorithm | Best | Average | Worst |
|----------------|------------|------------|------------|
| Quick sort | Ω(n log n) | Θ(n log n) | O(n^2) |
| Merge sort | Ω(n log n) | Θ(n log n) | O(n log n) |
| Heap sort | Ω(n log n) | Θ(n log n) | O(n log n) |
| Bubble sort | Ω(n) | Θ(n^2) | O(n^2) |
| Insertion sort | Ω(n) | Θ(n^2) | O(n^2) |
| Selection sort | Ω(n^2) | Θ(n^2) | O(n^2) |
| Bucket sort | Ω(n+k) | Θ(n+k) | O(n^ |