-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 6.9k
Elasticsearch cluster
This project supports a single-node Elasticsearch cluster by default. Following the instructions in this page, you will be able to scale out that cluster by adding extra nodes.
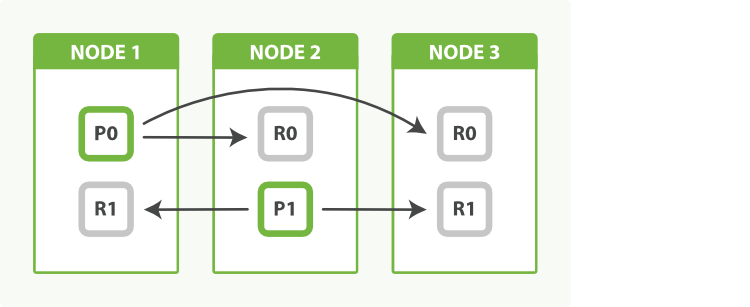
image source: Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide » Replica Shards
One must increase the vm.max_map_count kernel setting on all Docker hosts running Elasticsearch in order to pass the bootstrap checks triggered by the production mode. To do this, follow the recommended instructions from the Elastic documentation: Install Elasticsearch with Docker.
Using Docker Compose, the cluster will automatically bootstrap by discovering the other nodes running on the same machine. Simply proceed to the next steps. For more information, see Bootstrapping a cluster » Auto-bootstrapping in development mode.
FIXME: does not work because all instances listen on the same port (9200)
Both the discovery.seed_hosts and cluster.initial_master_nodes settings are necessary to bootstrap a cluster. It is possible to leverage the Docker internal DNS together with unicast Zen discovery mechanism in order to discover current cluster nodes. For that, simply set the discovery.seed_hosts Elasticsearch setting to the name of your Elasticsearch task, either in the elasticsearch.yml configuration file or via an environment variable.
For more information, see Important discovery and cluster formation settings.
Example (Swarm mode):
# docker-stack.yml
elasticsearch:
environment:
# set a predictable node name
node.name: elk_elasticsearch.{{.Task.Slot}}
# disable single-node discovery
discovery.type: ''
# use internal Docker round-robin DNS for unicast discovery
discovery.seed_hosts: tasks.elasticsearch
# define initial masters, assuming a cluster size of at least 3
cluster.initial_master_nodes: elk_elasticsearch.1,elk_elasticsearch.2,elk_elasticsearch.3The default docker-compose file uses static host port mapping for the elasticsearch service. This prevents scaling services because a single port can be mapped only once on the host. Instead, you have to either disable port mapping completely, or let Docker map container ports to random host ports in order to prevent clashes.
Example:
# docker-compose.yml
elasticsearch:
ports:
# map to random host ports instead of static ports, eg. 32000:9200
- '9200'
- '9300'In the default configuration, multiple Elasticsearch nodes are not allowed to share the same data volume. This limitation can be removed by setting the node.max_local_storage_nodes setting to the number of Elasticsearch nodes in the cluster.
Example:
# docker-compose.yml
elasticsearch:
environment:
node.max_local_storage_nodes: '3'Start the ELK stack with multiple elasticsearch replicas:
$ docker-compose up -d --scale elasticsearch=3
Creating docker-elk_elasticsearch_1 ... done
Creating docker-elk_elasticsearch_2 ... done
Creating docker-elk_elasticsearch_3 ... done
Creating docker-elk_kibana_1 ... done
Creating docker-elk_logstash_1 ... doneThe cluster should bootstrap:
$ docker logs docker-elk_elasticsearch_2
...
{"type": "server", "timestamp": "2019-11-07T23:43:28,818Z", "level": "INFO", "component": "o.e.c.s.ClusterApplierService", "cluster.name": "docker-cluster", "node.name": "elk_elasticsearch.2", "message": "master node changed {previous [], current [{elk_elasticsearch.1}{iaojnf4mQZyuhmGRzEdjaw}{uY0WaM9_SkOTGfawR2T2uQ}{10.0.3.9}{10.0.3.9:9300}{dilm}{ml.machine_memory=18334330880, ml.max_open_jobs=20, xpack.installed=true}]}, added {{elk_elasticsearch.1}{iaojnf4mQZyuhmGRzEdjaw}{uY0WaM9_SkOTGfawR2T2uQ}{10.0.3.9}{10.0.3.9:9300}{dilm}{ml.machine_memory=18334330880, ml.max_open_jobs=20, xpack.installed=true},{elk_elasticsearch.3}{IxmnhJE6S8qpX41co-iwhQ}{pKqmFTC_TqiqMsF3fLCGmw}{10.0.3.8}{10.0.3.8:9300}{dilm}{ml.machine_memory=18334330880, ml.max_open_jobs=20, xpack.installed=true},}, term: 2, version: 1, reason: ApplyCommitRequest{term=2, version=1, sourceNode={elk_elasticsearch.1}{iaojnf4mQZyuhmGRzEdjaw}{uY0WaM9_SkOTGfawR2T2uQ}{10.0.3.9}{10.0.3.9:9300}{dilm}{ml.machine_memory=18334330880, ml.max_open_jobs=20, xpack.installed=true}}" }All nodes will show up in Kibana's Monitoring app: