You are given two integers m and n representing the dimensions of a 0-indexed m x n grid.
You are also given a 0-indexed 2D integer matrix coordinates, where coordinates[i] = [x, y] indicates that the cell with coordinates [x, y] is colored black. All cells in the grid that do not appear in coordinates are white.
A block is defined as a 2 x 2 submatrix of the grid. More formally, a block with cell [x, y] as its top-left corner where 0 <= x < m - 1 and 0 <= y < n - 1 contains the coordinates [x, y], [x + 1, y], [x, y + 1], and [x + 1, y + 1].
Return a 0-indexed integer array arr of size 5 such that arr[i] is the number of blocks that contains exactly i black cells.
Example 1:
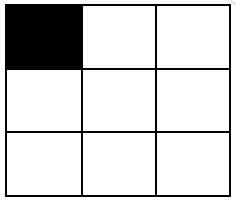
Input: m = 3, n = 3, coordinates = [[0,0]] Output: [3,1,0,0,0] Explanation: The grid looks like this:There is only 1 block with one black cell, and it is the block starting with cell [0,0]. The other 3 blocks start with cells [0,1], [1,0] and [1,1]. They all have zero black cells. Thus, we return [3,1,0,0,0].
Example 2:
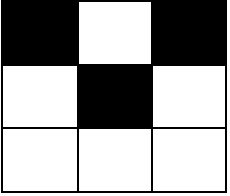
Input: m = 3, n = 3, coordinates = [[0,0],[1,1],[0,2]] Output: [0,2,2,0,0] Explanation: The grid looks like this:There are 2 blocks with two black cells (the ones starting with cell coordinates [0,0] and [0,1]). The other 2 blocks have starting cell coordinates of [1,0] and [1,1]. They both have 1 black cell. Therefore, we return [0,2,2,0,0].
Constraints:
2 <= m <= 1052 <= n <= 1050 <= coordinates.length <= 104coordinates[i].length == 20 <= coordinates[i][0] < m0 <= coordinates[i][1] < n- It is guaranteed that
coordinatescontains pairwise distinct coordinates.
Related Topics:
Array, Hash Table, Enumeration
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-black-blocks
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
vector<long long> countBlackBlocks(int m, int n, vector<vector<int>>& A) {
typedef long long LL;
int d[4][2] = {{0,0},{0,-1},{-1,0},{-1,-1}};
unordered_map<LL, int> cnt;
for (auto &v : A) {
LL x = v[0], y = v[1];
for (auto &[dx, dy] : d) {
LL a = x + dx, b = y + dy;
if (a < 0 || b < 0 || a >= m - 1 || b >= n - 1) continue;
cnt[a * (n - 1) + b]++;
}
}
vector<LL> ans(5);
for (auto &[_, c]: cnt) ans[c]++;
ans[0] = (LL)(m - 1) * (n - 1) - accumulate(begin(ans), end(ans), 0LL);
return ans;
}
};