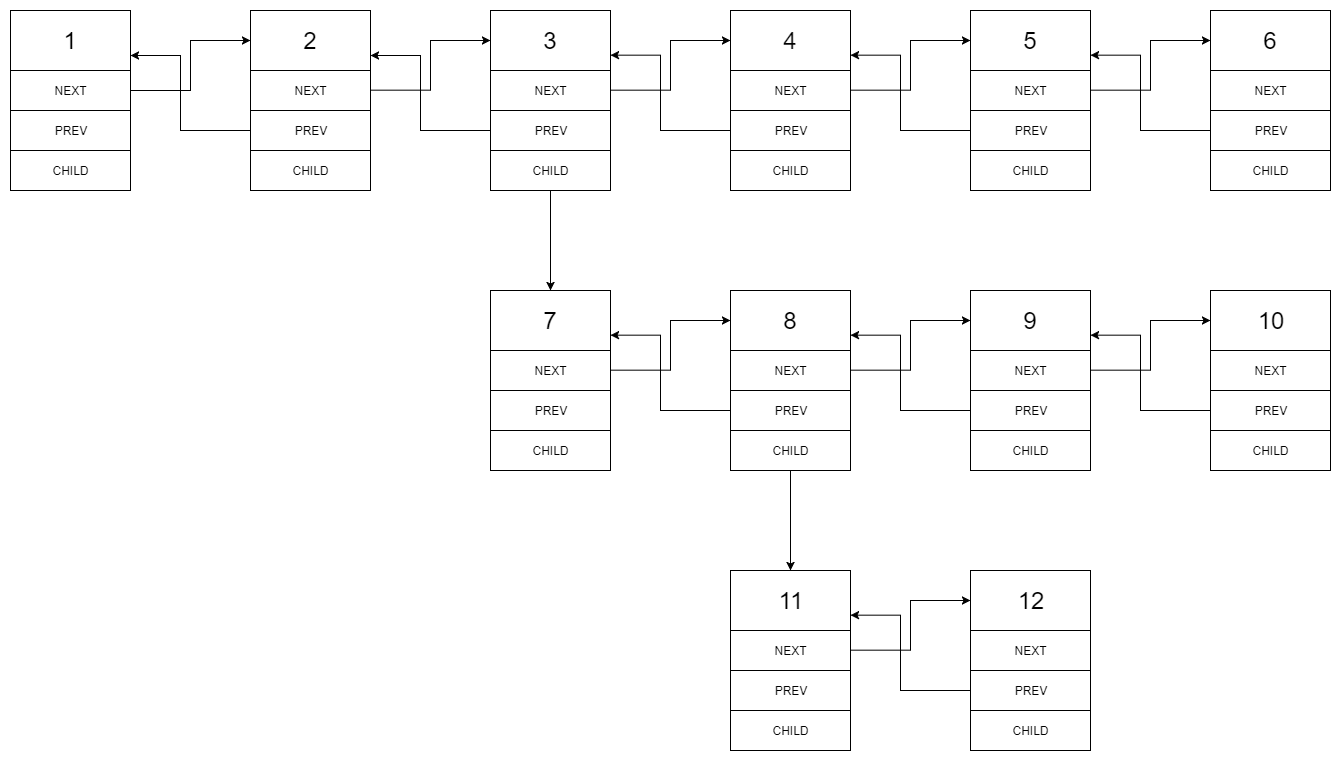
You are given a doubly linked list which in addition to the next and previous pointers, it could have a child pointer, which may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure, as shown in the example below.
Flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list. You are given the head of the first level of the list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12] Output: [1,2,3,7,8,11,12,9,10,4,5,6] Explanation: The multilevel linked list in the input is as follows:After flattening the multilevel linked list it becomes:

Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2,null,3] Output: [1,3,2] Explanation: The input multilevel linked list is as follows: 1---2---NULL | 3---NULL
Example 3:
Input: head = [] Output: []
How multilevel linked list is represented in test case:
We use the multilevel linked list from Example 1 above:
1---2---3---4---5---6--NULL
|
7---8---9---10--NULL
|
11--12--NULL
The serialization of each level is as follows:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null] [7,8,9,10,null] [11,12,null]
To serialize all levels together we will add nulls in each level to signify no node connects to the upper node of the previous level. The serialization becomes:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null] [null,null,7,8,9,10,null] [null,11,12,null]
Merging the serialization of each level and removing trailing nulls we obtain:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12]
Constraints:
- Number of Nodes will not exceed 1000.
1 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Related Topics:
Linked List, Depth-first Search
Similar Questions:
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-a-multilevel-doubly-linked-list/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
public:
Node* flatten(Node* head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
Node dummy, *tail = &dummy;
while (head) {
auto node = head;
head = head->next;
tail->next = node;
node->prev = tail;
tail = node;
if (node->child) {
auto next = flatten(node->child);
tail->next = next;
next->prev = tail;
while (tail->next) tail = tail->next;
}
node->child = NULL;
}
dummy.next->prev = NULL;
return dummy.next;
}
};// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-a-multilevel-doubly-linked-list/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
public:
Node* flatten(Node* head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
Node dummy, *tail = &dummy;
stack<Node*> s;
s.push(head);
while (s.size()) {
auto node = s.top(), child = node->child;
tail->next = node;
node->prev = tail;
tail = node;
node->child = NULL;
if (node->next) s.top() = node->next;
else s.pop();
if (child) s.push(child);
}
dummy.next->prev = NULL;
return dummy.next;
}
};Return a pair of pointers to first node and last node so that we don't need to traversel the flattened child again during the recursion.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-a-multilevel-doubly-linked-list/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H) where H is the max depth of the child hierarchy.
class Solution {
pair<Node*, Node*> dfs(Node* head) {
if (!head) return {NULL, NULL};
pair<Node*, Node*> p = {head, NULL}; // first node, last node.
while (head) {
auto next = head->next;
auto last = head;
if (head->child) {
auto q = dfs(head->child);
head->next = q.first;
q.first->prev = head;
if (next) {
q.second->next = next;
next->prev = q.second;
} else last = q.second;
head->child = NULL;
}
if (!next) p.second = last;
head = next;
}
return p;
}
public:
Node* flatten(Node* head) {
return dfs(head).first;
}
};// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-a-multilevel-doubly-linked-list/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
Node* flatten(Node* head) {
for (auto p = head; p; p = p->next) {
if (!p->child) continue;
auto next = p->next, q = p->child;
p->next = q;
q->prev = p;
while (q->next) q = q->next;
q->next = next;
if (next) next->prev = q;
p->child = NULL;
}
return head;
}
};