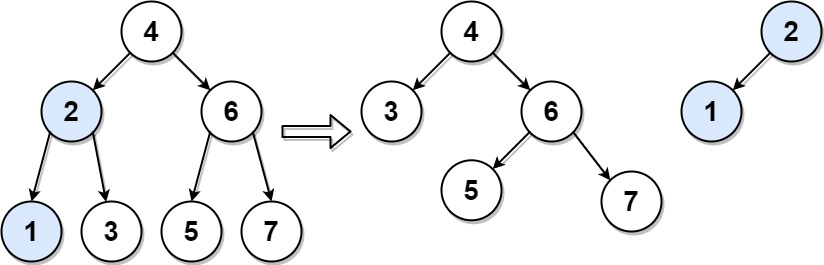
Given the root of a binary search tree (BST) and an integer target, split the tree into two subtrees where one subtree has nodes that are all smaller or equal to the target value, while the other subtree has all nodes that are greater than the target value. It Is not necessarily the case that the tree contains a node with the value target.
Additionally, most of the structure of the original tree should remain. Formally, for any child c with parent p in the original tree, if they are both in the same subtree after the split, then node c should still have the parent p.
Return an array of the two roots of the two subtrees.
Example 1:
Input: root = [4,2,6,1,3,5,7], target = 2 Output: [[2,1],[4,3,6,null,null,5,7]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1], target = 1 Output: [[1],[]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 50]. 0 <= Node.val, target <= 1000
Companies: Google, Amazon, Coupang
Related Topics:
Tree, Binary Search Tree, Recursion, Binary Tree
Similar Questions:
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/split-bst
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N^2)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
vector<TreeNode*> splitBST(TreeNode* root, int target) {
TreeNode *left = nullptr, *right = nullptr;
function<void(TreeNode*, TreeNode*)> add = [&](TreeNode *root, TreeNode *n) {
if (n->val > root->val) {
if (root->right) add(root->right, n);
else root->right = n;
} else {
if (root->left) add(root->left, n);
else root->left = n;
}
};
function<void(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode *root) {
if (!root) return;
auto L = root->left, R = root->right;
root->left = root->right = nullptr;
if (root->val <= target) {
if (!left) left = root;
else add(left, root);
} else {
if (!right) right = root;
else add(right, root);
}
dfs(L);
dfs(R);
};
dfs(root);
return {left, right};
}
};// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/split-bst
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
public:
vector<TreeNode*> splitBST(TreeNode* root, int target) {
if (!root) return {nullptr, nullptr};
if (root->val == target) {
auto r = root->right;
root->right = nullptr;
return {root, r};
}
if (root->val < target) {
auto v = splitBST(root->right, target);
root->right = v[0];
return {root, v[1]};
} else {
auto v = splitBST(root->left, target);
root->left = v[1];
return {v[0], root};
}
}
};