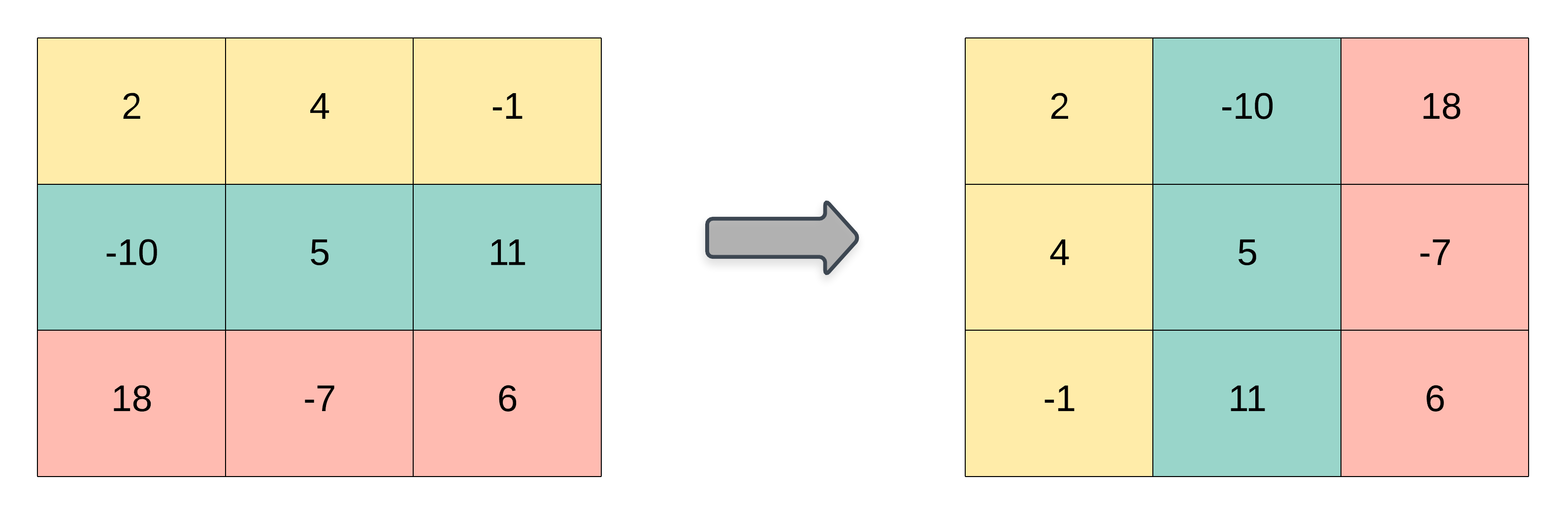
Given a 2D integer array matrix, return the transpose of matrix.
The transpose of a matrix is the matrix flipped over its main diagonal, switching the matrix's row and column indices.
Example 1:
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] Output: [[1,4,7],[2,5,8],[3,6,9]]
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]] Output: [[1,4],[2,5],[3,6]]
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10001 <= m * n <= 105-109 <= matrix[i][j] <= 109
Companies: Amazon, Bloomberg, Apple, Citadel
Related Topics:
Array, Matrix, Simulation
Hints:
- We don't need any special algorithms to do this. You just need to know what the transpose of a matrix looks like. Rows become columns and vice versa!
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/transpose-matrix/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(MN)
// Space: O(1) extra space
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> transpose(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
int M = A.size(), N = A[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> ans(N, vector<int>(M));
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
ans[j][i] = A[i][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
};