# ROSNS3: A Network Simulator (NS-3) bridge for Robot Operating System (ROS)
This is an NS-3 extension for ROS that allows to simulate network aspects of a robot swarm. Briefly, [NS-3](https://www.nsnam.org/) is an event simulator to design and implement network models. ROSNS-3 allows to
- Simulate wireless signal attenuation,
- Perform network packet routing,
- Calculating recieved signal strength (RSS) between nodes,
- Retrieve updated routing tables in real-time.
Consider citing our work [1] if you find this code helpful for your publications.
## System Overview
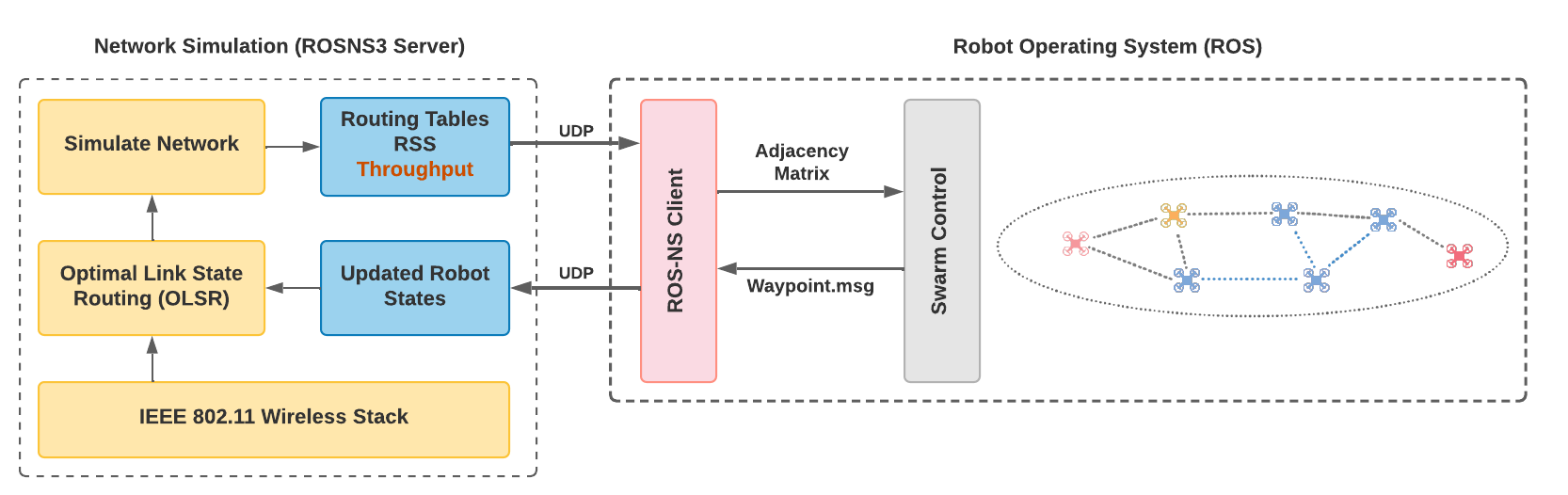
- The ROS and NS-3 environments simulate the robots’ movements, and the network events, respectively.
- ROSNS3 establishes the communication between the two environments using the UDP.
- Currently, to calculate the routing paths as the robots move, we use Optimized Link State Routing (OLSR) algorithm.
- RSS and throughput features are planned for future work.
## Run ROSNS3
### Clone ROSNS3
Clone ROSNS3 to your `catkin_ws/src` using the command below.
- `git clone --recursive git@github.com:malintha/rosns3.git`
ROSNS3 relies on both the client and server modules. To avoid having to install bulky NS-3 software, we have provided a dockerized version of the ROSNS3 server. Unless you need to change the server code, which resides at `rosns3_server` there is no need to explicitly build it.
- Download the docker image by running `docker pull malinthaf/rosns3-server:latest`.
You can change the propagation loss model parameters for wireless communiation inside the `run_server.sh` script. These changes will subsequently applied to the server running inside the docker container.
### Build ROSNS3 Client
- Simply run `catkin build rosns3_client`.
### Run
- Run `./run_server.sh` to run the server.
- By default, the rosns3_server will run on the UDP port `28500`.
- Run the client with command `roslaunch rosns3_client rosns3_client.launch n_backbone:=5` to simulate the adhoc wireless communication in a robot swarm of 5 nodes.
- To stop the server run `stop_server.sh` script. This will kill the ROSNS3 server, stop the docker container, and remove the it from memory.
### Usage
- ROSNS3 uses `rostopics` to obtain the swarm's physical state from the ROS-enabled physics simulator. More specifically, in your simulation platform each robot can publish its state to the topic `/robot_<robot_id>/current_state`. For now you can use the message type `rosns3_client/Waypoint` for the communication. In future releases we plan to change this to a more generic ros_std type.
- Internally, the client aggregates the robots' states periodically and communicates it to the server using a flatbuffers message type.
- The server calculates the current communication topology of the swarm using the Friis wireless channel model and OLSR routing, and publishes it to the topic `/rosns3_client/routing_table`.
- Each entry in the routing table corresponds to the adjacency matrix, and specifies the number of communication hops between the two given robots in the swarm.
## References
[1] @ARTICLE{9739846,
author={Fernando, Malintha and Senanayake, Ransalu and Swany, Martin},
journal={IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters},
title={CoCo Games: Graphical Game-Theoretic Swarm Control for Communication-Aware Coverage},
year={2022},
volume={7},
number={3},
pages={5966-5973},
doi={10.1109/LRA.2022.3160968}}