This network-scanner does basically is , it scans the network and shows how many devices are connected to that network and what is their id address and mac address.
- Linux OS
- Scapy
- argprase
-
First, we need to install scapy.Then we gonna need to import essential methods from scapy:
from scapy.all import scapy -
Second import argprase
import argprase -
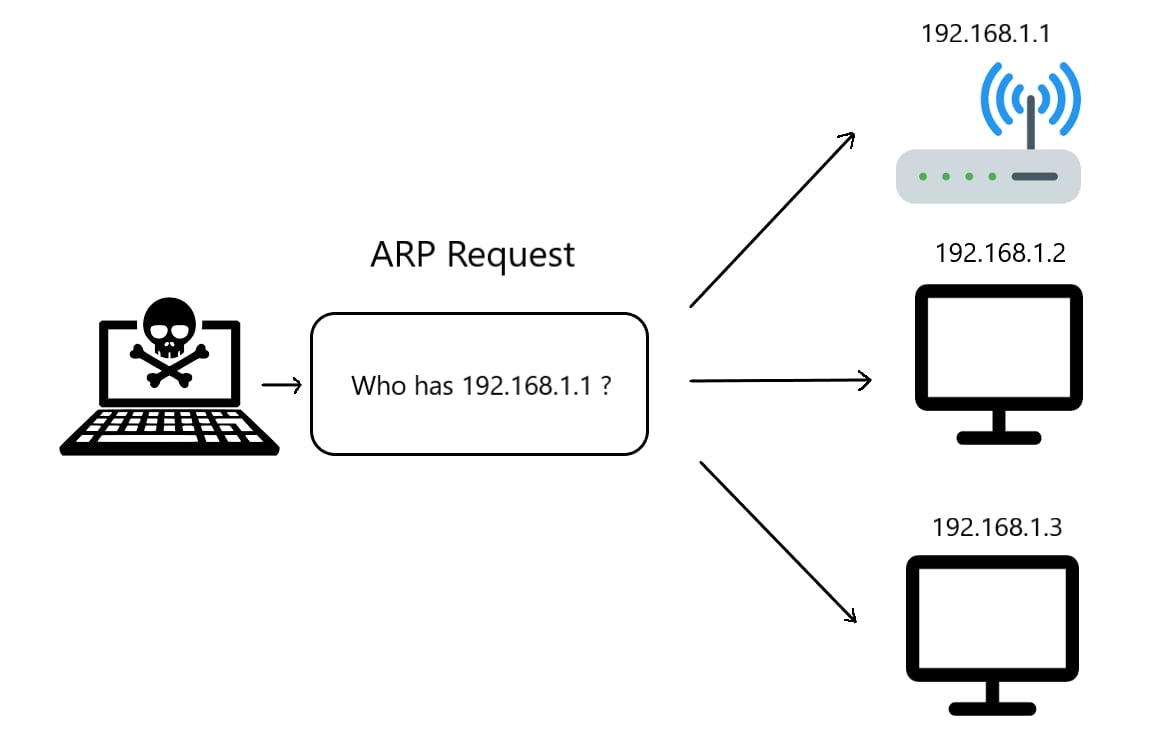
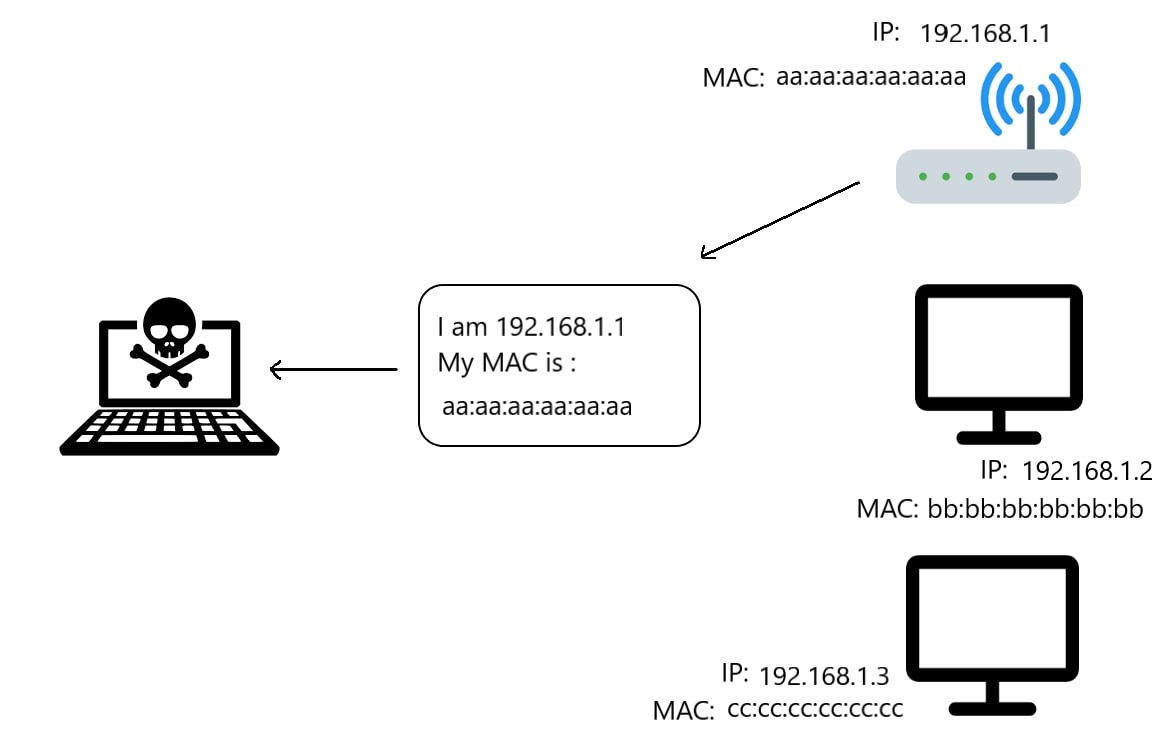
Third, we gonna need to make an ARP request as shown in the following image:
The arp example is like shown in the follwowing image:
So lets create packets:
def scan_network(target_ip):
arp_request = scapy.ARP(pdst=target_ip) # Creating ARP packets.
broadcast = scapy.Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")
packet = broadcast/arp_request
ask_list = scapy.srp(packet, timeout = 3, verbose = False)[0]
Now we have created these packets, we need to send them using srp() function which sends and receives packets at layer 2, we set the timeout to 3 so the script won't get stuck:
ask_list = scapy.srp(packet, timeout = 3, verbose = False)[0]
Result now is a list of pairs that is of the format (sent_packet, received_packet), let's iterate over them:
packet_list = []
for i in ask_list:
packet_dict = {"ip" : i[1].psrc, "mac" : i[1].hwsrc}
packet_list.append(packet_dict)
return(packet_list)
Now lets Print:
def print_res(res):
print(""" __ _ ___ _____ _ _ __ ___ _ __ __ ___ __ __ _ __ _ ___ ___
| \| | __|_ _| | | |/__\| _ \ |/ / /' _/ / _// \| \| | \| | __| _ \
| | ' | _| | | | 'V' | \/ | v / < `._`.| \_| /\ | | ' | | ' | _|| v /
|_|\__|___| |_| !_/ \_!\__/|_|_\_|\_\ |___/ \__/_||_|_|\__|_|\__|___|_|_\ """)
print("=========================================")
print("IP\t\t\tMAC Address\n=========================================")
for n in res:
print(n["ip"] + "\t\t" + n["mac"])
To Run :
python NetworkScanner.py -i IP address/24