forked from apache/spark
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 6
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
[SPARK-31030][SQL] Backward Compatibility for Parsing and formatting …
…Datetime In Spark version 2.4 and earlier, datetime parsing, formatting and conversion are performed by using the hybrid calendar (Julian + Gregorian). Since the Proleptic Gregorian calendar is de-facto calendar worldwide, as well as the chosen one in ANSI SQL standard, Spark 3.0 switches to it by using Java 8 API classes (the java.time packages that are based on ISO chronology ). The switching job is completed in SPARK-26651. But after the switching, there are some patterns not compatible between Java 8 and Java 7, Spark needs its own definition on the patterns rather than depends on Java API. In this PR, we achieve this by writing the document and shadow the incompatible letters. See more details in [SPARK-31030](https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/SPARK-31030) For backward compatibility. No. After we define our own datetime parsing and formatting patterns, it's same to old Spark version. Existing and new added UT. Locally document test: 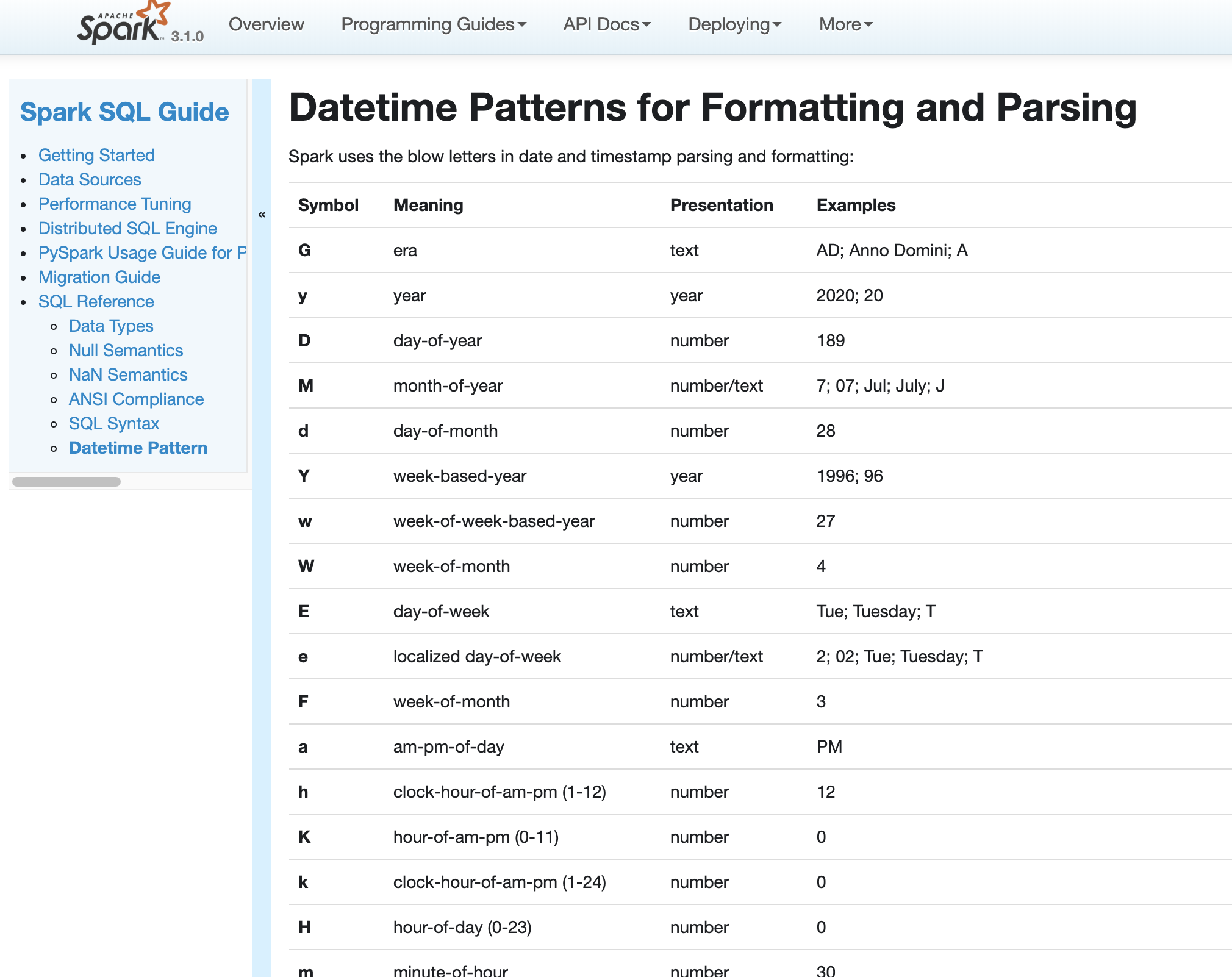 Closes apache#27830 from xuanyuanking/SPARK-31030. Authored-by: Yuanjian Li <[email protected]> Signed-off-by: Wenchen Fan <[email protected]> (cherry picked from commit 3493162) Signed-off-by: Wenchen Fan <[email protected]>
- Loading branch information
1 parent
3f23529
commit 202fe11
Showing
19 changed files
with
341 additions
and
66 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,220 @@ | ||
| --- | ||
| layout: global | ||
| title: Datetime patterns | ||
| displayTitle: Datetime Patterns for Formatting and Parsing | ||
| license: | | ||
| Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more | ||
| contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with | ||
| this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. | ||
| The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 | ||
| (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with | ||
| the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at | ||
| http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 | ||
| Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software | ||
| distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, | ||
| WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. | ||
| See the License for the specific language governing permissions and | ||
| limitations under the License. | ||
| --- | ||
|
|
||
| There are several common scenarios for datetime usage in Spark: | ||
|
|
||
| - CSV/JSON datasources use the pattern string for parsing and formatting time content. | ||
|
|
||
| - Datetime functions related to convert string to/from `DateType` or `TimestampType`. For example, unix_timestamp, date_format, to_unix_timestamp, from_unixtime, to_date, to_timestamp, from_utc_timestamp, to_utc_timestamp, etc. | ||
|
|
||
| Spark uses the below letters in date and timestamp parsing and formatting: | ||
| <table class="table"> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <th> <b>Symbol</b> </th> | ||
| <th> <b>Meaning</b> </th> | ||
| <th> <b>Presentation</b> </th> | ||
| <th> <b>Examples</b> </th> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>G</b> </td> | ||
| <td> era </td> | ||
| <td> text </td> | ||
| <td> AD; Anno Domini; A </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>y</b> </td> | ||
| <td> year </td> | ||
| <td> year </td> | ||
| <td> 2020; 20 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>D</b> </td> | ||
| <td> day-of-year </td> | ||
| <td> number </td> | ||
| <td> 189 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>M</b> </td> | ||
| <td> month-of-year </td> | ||
| <td> number/text </td> | ||
| <td> 7; 07; Jul; July; J </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>d</b> </td> | ||
| <td> day-of-month </td> | ||
| <td> number </td> | ||
| <td> 28 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>Y</b> </td> | ||
| <td> week-based-year </td> | ||
| <td> year </td> | ||
| <td> 1996; 96 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>w</b> </td> | ||
| <td> week-of-week-based-year </td> | ||
| <td> number </td> | ||
| <td> 27 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>W</b> </td> | ||
| <td> week-of-month </td> | ||
| <td> number </td> | ||
| <td> 4 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>E</b> </td> | ||
| <td> day-of-week </td> | ||
| <td> text </td> | ||
| <td> Tue; Tuesday; T </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>e</b> </td> | ||
| <td> localized day-of-week </td> | ||
| <td> number/text </td> | ||
| <td> 2; 02; Tue; Tuesday; T </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>F</b> </td> | ||
| <td> week-of-month </td> | ||
| <td> number </td> | ||
| <td> 3 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>a</b> </td> | ||
| <td> am-pm-of-day </td> | ||
| <td> text </td> | ||
| <td> PM </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>h</b> </td> | ||
| <td> clock-hour-of-am-pm (1-12) </td> | ||
| <td> number </td> | ||
| <td> 12 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>K</b> </td> | ||
| <td> hour-of-am-pm (0-11) </td> | ||
| <td> number </td> | ||
| <td> 0 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>k</b> </td> | ||
| <td> clock-hour-of-day (1-24) </td> | ||
| <td> number </td> | ||
| <td> 0 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>H</b> </td> | ||
| <td> hour-of-day (0-23) </td> | ||
| <td> number </td> | ||
| <td> 0 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>m</b> </td> | ||
| <td> minute-of-hour </td> | ||
| <td> number </td> | ||
| <td> 30 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>s</b> </td> | ||
| <td> second-of-minute </td> | ||
| <td> number </td> | ||
| <td> 55 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>S</b> </td> | ||
| <td> fraction-of-second </td> | ||
| <td> fraction </td> | ||
| <td> 978 </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>z</b> </td> | ||
| <td> time-zone name </td> | ||
| <td> zone-name </td> | ||
| <td> Pacific Standard Time; PST </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>O</b> </td> | ||
| <td> localized zone-offset </td> | ||
| <td> offset-O </td> | ||
| <td> GMT+8; GMT+08:00; UTC-08:00; </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>X</b> </td> | ||
| <td> zone-offset 'Z' for zero </td> | ||
| <td> offset-X </td> | ||
| <td> Z; -08; -0830; -08:30; -083015; -08:30:15; </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>x</b> </td> | ||
| <td> zone-offset </td> | ||
| <td> offset-x </td> | ||
| <td> +0000; -08; -0830; -08:30; -083015; -08:30:15; </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>Z</b> </td> | ||
| <td> zone-offset </td> | ||
| <td> offset-Z </td> | ||
| <td> +0000; -0800; -08:00; </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>'</b> </td> | ||
| <td> escape for text </td> | ||
| <td> delimiter </td> | ||
| <td></td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| <tr> | ||
| <td> <b>''</b> </td> | ||
| <td> single quote </td> | ||
| <td> literal </td> | ||
| <td> ' </td> | ||
| </tr> | ||
| </table> | ||
|
|
||
| The count of pattern letters determines the format. | ||
|
|
||
| - Text: The text style is determined based on the number of pattern letters used. Less than 4 pattern letters will use the short form. Exactly 4 pattern letters will use the full form. Exactly 5 pattern letters will use the narrow form. Six or more letters will fail. | ||
|
|
||
| - Number: If the count of letters is one, then the value is output using the minimum number of digits and without padding. Otherwise, the count of digits is used as the width of the output field, with the value zero-padded as necessary. The following pattern letters have constraints on the count of letters. Only one letter 'F' can be specified. Up to two letters of 'd', 'H', 'h', 'K', 'k', 'm', and 's' can be specified. Up to three letters of 'D' can be specified. | ||
|
|
||
| - Number/Text: If the count of pattern letters is 3 or greater, use the Text rules above. Otherwise use the Number rules above. | ||
|
|
||
| - Fraction: Outputs the micro-of-second field as a fraction-of-second. The micro-of-second value has six digits, thus the count of pattern letters is from 1 to 6. If it is less than 6, then the micro-of-second value is truncated, with only the most significant digits being output. | ||
|
|
||
| - Year: The count of letters determines the minimum field width below which padding is used. If the count of letters is two, then a reduced two digit form is used. For printing, this outputs the rightmost two digits. For parsing, this will parse using the base value of 2000, resulting in a year within the range 2000 to 2099 inclusive. If the count of letters is less than four (but not two), then the sign is only output for negative years. Otherwise, the sign is output if the pad width is exceeded when 'G' is not present. | ||
|
|
||
| - Zone names: This outputs the display name of the time-zone ID. If the count of letters is one, two or three, then the short name is output. If the count of letters is four, then the full name is output. Five or more letters will fail. | ||
|
|
||
| - Offset X and x: This formats the offset based on the number of pattern letters. One letter outputs just the hour, such as '+01', unless the minute is non-zero in which case the minute is also output, such as '+0130'. Two letters outputs the hour and minute, without a colon, such as '+0130'. Three letters outputs the hour and minute, with a colon, such as '+01:30'. Four letters outputs the hour and minute and optional second, without a colon, such as '+013015'. Five letters outputs the hour and minute and optional second, with a colon, such as '+01:30:15'. Six or more letters will fail. Pattern letter 'X' (upper case) will output 'Z' when the offset to be output would be zero, whereas pattern letter 'x' (lower case) will output '+00', '+0000', or '+00:00'. | ||
|
|
||
| - Offset O: This formats the localized offset based on the number of pattern letters. One letter outputs the short form of the localized offset, which is localized offset text, such as 'GMT', with hour without leading zero, optional 2-digit minute and second if non-zero, and colon, for example 'GMT+8'. Four letters outputs the full form, which is localized offset text, such as 'GMT, with 2-digit hour and minute field, optional second field if non-zero, and colon, for example 'GMT+08:00'. Any other count of letters will fail. | ||
|
|
||
| - Offset Z: This formats the offset based on the number of pattern letters. One, two or three letters outputs the hour and minute, without a colon, such as '+0130'. The output will be '+0000' when the offset is zero. Four letters outputs the full form of localized offset, equivalent to four letters of Offset-O. The output will be the corresponding localized offset text if the offset is zero. Five letters outputs the hour, minute, with optional second if non-zero, with colon. It outputs 'Z' if the offset is zero. Six or more letters will fail. | ||
|
|
||
| More details for the text style: | ||
|
|
||
| - Short Form: Short text, typically an abbreviation. For example, day-of-week Monday might output "Mon". | ||
|
|
||
| - Full Form: Full text, typically the full description. For example, day-of-week Monday might output "Monday". | ||
|
|
||
| - Narrow Form: Narrow text, typically a single letter. For example, day-of-week Monday might output "M". |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
Oops, something went wrong.