Correlation Attacks of an LFSR based Stream Cipher in Python.
The program uses argparse. You need to pass a value for each following parameter:
- -S, --polynomialsize: Number of bits of the polynomial.
- -k, --keystream: Keystream in hexadecimal.
- -s, --keystreamsize: Number of bits of the keystream.
- -p, --xorposition: Positions of the bits to be xor, separated by spaces (start at 0 from the right)
For example:
python3 lfsr.py --polynomialsize <size> --keystream <keystream> --keystreamsize <size> --xorposition <pos pos ...>Consider a 64-bit combination generator with three LFSRs respectively having the following characteristic polynomials:
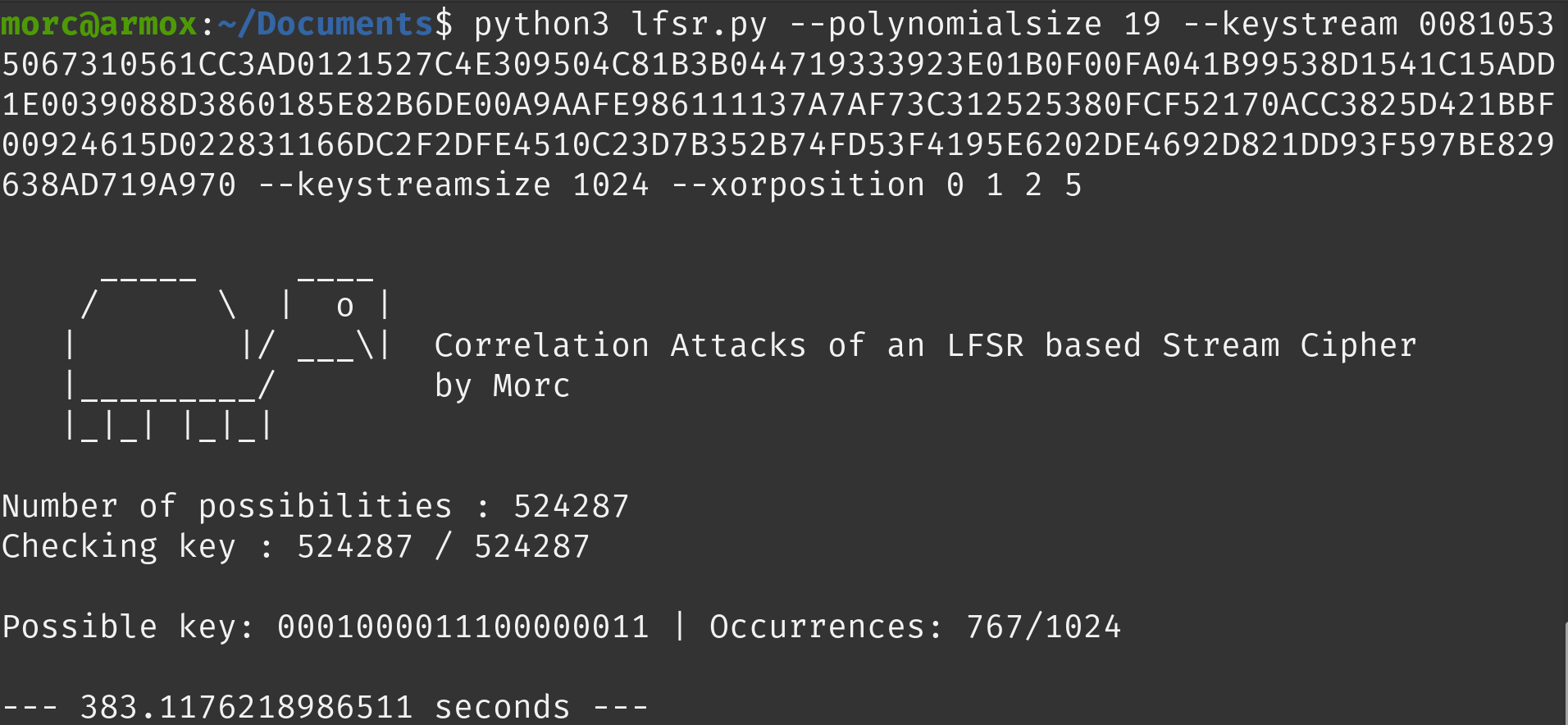
- x^19 + x^5 + x^2 + x + 1
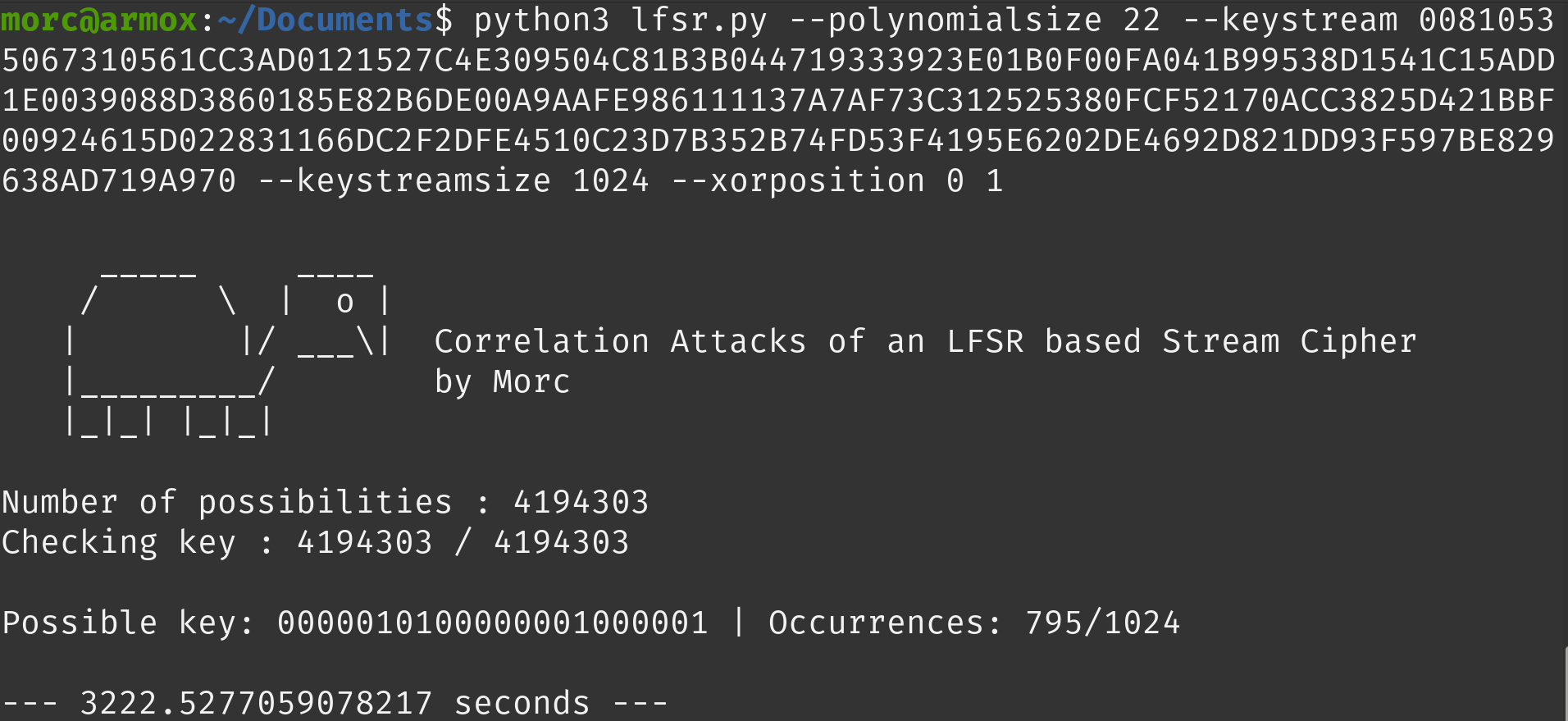
- x^22 + x + 1
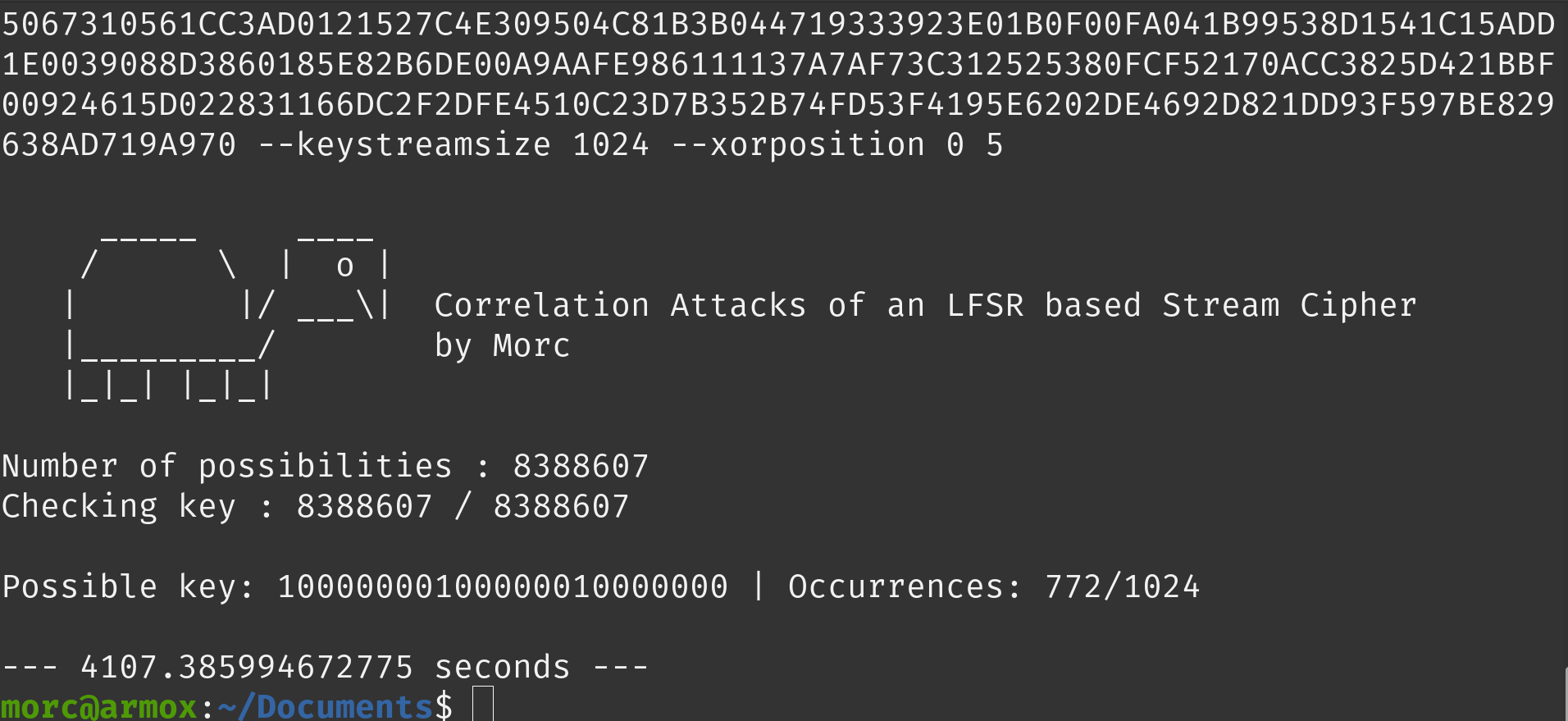
- x^23 + x^5 + 1
Suppose we have obtained the following 1024 bits of the keystream:
0x00810535067310561CC3AD0121527C4E309504C81B3B044719333923E01B0F00FA041B99538D1541C15ADD1E0039088D3860185E82B6DE00A9AAFE986111137A7AF73C312525380FCF52170ACC3825D421BBF00924615D022831166DC2F2DFE4510C23D7B352B74FD53F4195E6202DE4692D821DD93F597BE829638AD719A970
To recover the key, we need to generate the part of key with the help of the keystream and polynomials. Each polynomial generates a part of the key.
- Calcul LFSR
- The first step is calculating the LFSR of the polynomial to get all periods.
- Number of periods are number of possibilities.
- Generate bits stream for all possibilities
- The second step is generating bits stream for each period.
- To proceed, for each period, loop from the current period and get the last bit of each period until you have same number of bits than keystream size.
- Compare generated bits stream with the keystream
- For each generated bits stream, compare them with the keystream and count the number of occurrences of each same bit.
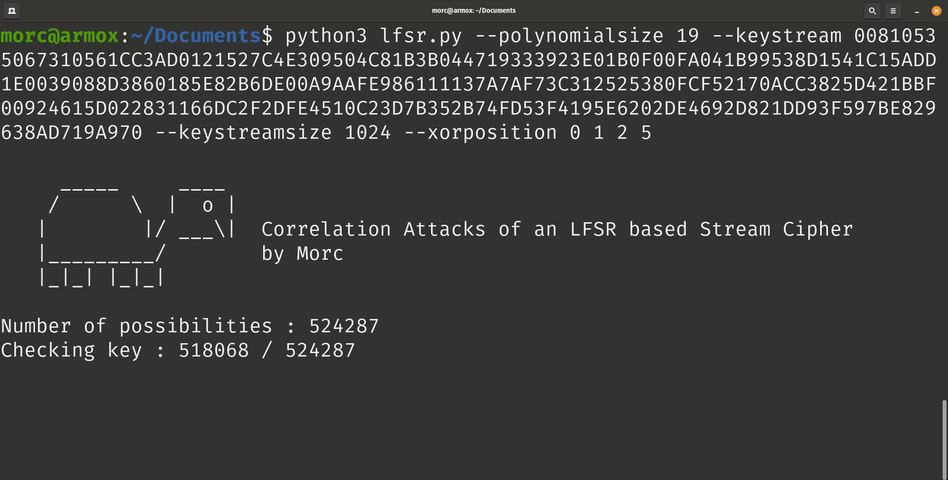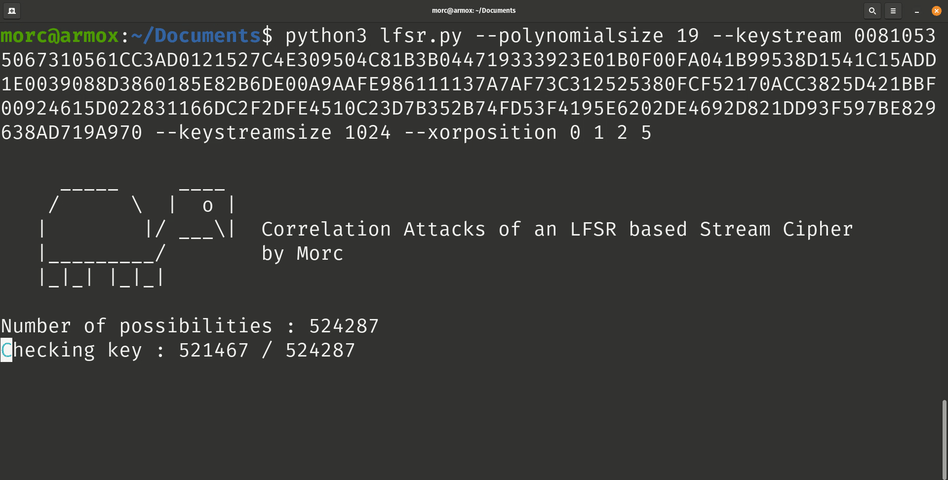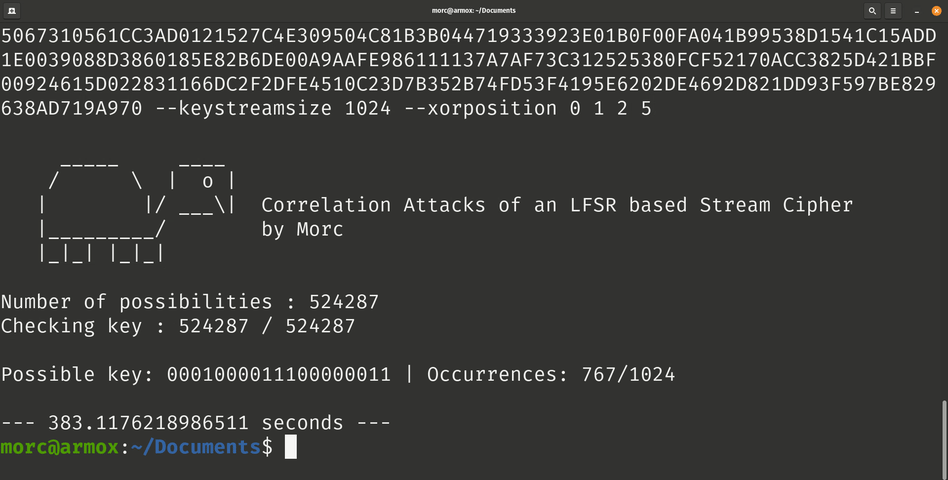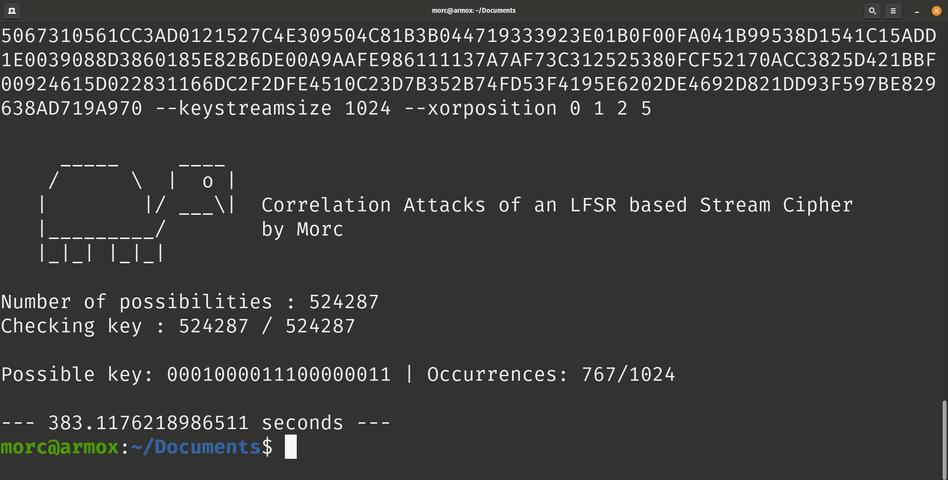
- The generated bits stream with the best occurrences contains the possible key in the beginning (the possible key has the same number of bits than number of bits of polynomial).
- Repeat previous steps for all polynomials
- Recover the key
- Put all possible key together to get the key
The first polynomial is: x^19 + x^5 + x^2 + x + 1. The key found is: 0001000011100000011.
The second polynomial is: x^22 + x + 1. The key found is: 0000010100000001000001.
The third polynomial is: x^23 + x^5 + 1. The key found is: 10000000100000010000000.
The 64-bit key is: 0001000011100000011000001010000000100000110000000100000010000000 or 0x10E060A020C04080 in hexadecimal.