forked from microsoft/nni
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Merge pull request #217 from microsoft/master
merge master
- Loading branch information
Showing
21 changed files
with
857 additions
and
153 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,54 @@ | ||
| L1FilterPruner on NNI Compressor | ||
| === | ||
|
|
||
| ## 1. Introduction | ||
|
|
||
| L1FilterPruner is a general structured pruning algorithm for pruning filters in the convolutional layers. | ||
|
|
||
| In ['PRUNING FILTERS FOR EFFICIENT CONVNETS'](https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.08710), authors Hao Li, Asim Kadav, Igor Durdanovic, Hanan Samet and Hans Peter Graf. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| > L1Filter Pruner prunes filters in the **convolution layers** | ||
| > | ||
| > The procedure of pruning m filters from the ith convolutional layer is as follows: | ||
| > | ||
| > 1. For each filter , calculate the sum of its absolute kernel weights | ||
| > 2. Sort the filters by 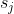. | ||
| > 3. Prune 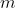 filters with the smallest sum values and their corresponding feature maps. The | ||
| > kernels in the next convolutional layer corresponding to the pruned feature maps are also | ||
| > removed. | ||
| > 4. A new kernel matrix is created for both the 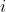th and 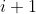th layers, and the remaining kernel | ||
| > weights are copied to the new model. | ||
| ## 2. Usage | ||
|
|
||
| PyTorch code | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| from nni.compression.torch import L1FilterPruner | ||
| config_list = [{ 'sparsity': 0.8, 'op_types': ['Conv2d'], 'op_names': ['conv1', 'conv2'] }] | ||
| pruner = L1FilterPruner(model, config_list) | ||
| pruner.compress() | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| #### User configuration for L1Filter Pruner | ||
|
|
||
| - **sparsity:** This is to specify the sparsity operations to be compressed to | ||
| - **op_types:** Only Conv2d is supported in L1Filter Pruner | ||
|
|
||
| ## 3. Experiment | ||
|
|
||
| We implemented one of the experiments in ['PRUNING FILTERS FOR EFFICIENT CONVNETS'](https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.08710), we pruned **VGG-16** for CIFAR-10 to **VGG-16-pruned-A** in the paper, in which $64\%$ parameters are pruned. Our experiments results are as follows: | ||
|
|
||
| | Model | Error(paper/ours) | Parameters | Pruned | | ||
| | --------------- | ----------------- | --------------- | -------- | | ||
| | VGG-16 | 6.75/6.49 | 1.5x10^7 | | | ||
| | VGG-16-pruned-A | 6.60/6.47 | 5.4x10^6 | 64.0% | | ||
|
|
||
| The experiments code can be found at [examples/model_compress]( https://github.com/microsoft/nni/tree/master/examples/model_compress/) | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,39 @@ | ||
| SlimPruner on NNI Compressor | ||
| === | ||
|
|
||
| ## 1. Slim Pruner | ||
|
|
||
| SlimPruner is a structured pruning algorithm for pruning channels in the convolutional layers by pruning corresponding scaling factors in the later BN layers. | ||
|
|
||
| In ['Learning Efficient Convolutional Networks through Network Slimming'](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.06519.pdf), authors Zhuang Liu, Jianguo Li, Zhiqiang Shen, Gao Huang, Shoumeng Yan and Changshui Zhang. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| > Slim Pruner **prunes channels in the convolution layers by masking corresponding scaling factors in the later BN layers**, L1 regularization on the scaling factors should be applied in batch normalization (BN) layers while training, scaling factors of BN layers are **globally ranked** while pruning, so the sparse model can be automatically found given sparsity. | ||
| ## 2. Usage | ||
|
|
||
| PyTorch code | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| from nni.compression.torch import SlimPruner | ||
| config_list = [{ 'sparsity': 0.8, 'op_types': ['BatchNorm2d'] }] | ||
| pruner = SlimPruner(model, config_list) | ||
| pruner.compress() | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| #### User configuration for Filter Pruner | ||
|
|
||
| - **sparsity:** This is to specify the sparsity operations to be compressed to | ||
| - **op_types:** Only BatchNorm2d is supported in Slim Pruner | ||
|
|
||
| ## 3. Experiment | ||
|
|
||
| We implemented one of the experiments in ['Learning Efficient Convolutional Networks through Network Slimming'](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.06519.pdf), we pruned $70\%$ channels in the **VGGNet** for CIFAR-10 in the paper, in which $88.5\%$ parameters are pruned. Our experiments results are as follows: | ||
|
|
||
| | Model | Error(paper/ours) | Parameters | Pruned | | ||
| | ------------- | ----------------- | ---------- | --------- | | ||
| | VGGNet | 6.34/6.40 | 20.04M | | | ||
| | Pruned-VGGNet | 6.20/6.39 | 2.03M | 88.5% | | ||
|
|
||
| The experiments code can be found at [examples/model_compress]( https://github.com/microsoft/nni/tree/master/examples/model_compress/) |
Loading
Sorry, something went wrong. Reload?
Sorry, we cannot display this file.
Sorry, this file is invalid so it cannot be displayed.
Loading
Sorry, something went wrong. Reload?
Sorry, we cannot display this file.
Sorry, this file is invalid so it cannot be displayed.
173 changes: 173 additions & 0 deletions
173
examples/model_compress/L1_filter_pruner_torch_vgg16.py
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,173 @@ | ||
| import math | ||
| import torch | ||
| import torch.nn as nn | ||
| import torch.nn.functional as F | ||
| from torchvision import datasets, transforms | ||
| from nni.compression.torch import L1FilterPruner | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| class vgg(nn.Module): | ||
| def __init__(self, init_weights=True): | ||
| super(vgg, self).__init__() | ||
| cfg = [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512] | ||
| self.cfg = cfg | ||
| self.feature = self.make_layers(cfg, True) | ||
| num_classes = 10 | ||
| self.classifier = nn.Sequential( | ||
| nn.Linear(cfg[-1], 512), | ||
| nn.BatchNorm1d(512), | ||
| nn.ReLU(inplace=True), | ||
| nn.Linear(512, num_classes) | ||
| ) | ||
| if init_weights: | ||
| self._initialize_weights() | ||
|
|
||
| def make_layers(self, cfg, batch_norm=True): | ||
| layers = [] | ||
| in_channels = 3 | ||
| for v in cfg: | ||
| if v == 'M': | ||
| layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)] | ||
| else: | ||
| conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False) | ||
| if batch_norm: | ||
| layers += [conv2d, nn.BatchNorm2d(v), nn.ReLU(inplace=True)] | ||
| else: | ||
| layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)] | ||
| in_channels = v | ||
| return nn.Sequential(*layers) | ||
|
|
||
| def forward(self, x): | ||
| x = self.feature(x) | ||
| x = nn.AvgPool2d(2)(x) | ||
| x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) | ||
| y = self.classifier(x) | ||
| return y | ||
|
|
||
| def _initialize_weights(self): | ||
| for m in self.modules(): | ||
| if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): | ||
| n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels | ||
| m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n)) | ||
| if m.bias is not None: | ||
| m.bias.data.zero_() | ||
| elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): | ||
| m.weight.data.fill_(0.5) | ||
| m.bias.data.zero_() | ||
| elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): | ||
| m.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01) | ||
| m.bias.data.zero_() | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| def train(model, device, train_loader, optimizer): | ||
| model.train() | ||
| for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader): | ||
| data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device) | ||
| optimizer.zero_grad() | ||
| output = model(data) | ||
| loss = F.cross_entropy(output, target) | ||
| loss.backward() | ||
| optimizer.step() | ||
| if batch_idx % 100 == 0: | ||
| print('{:2.0f}% Loss {}'.format(100 * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item())) | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| def test(model, device, test_loader): | ||
| model.eval() | ||
| test_loss = 0 | ||
| correct = 0 | ||
| with torch.no_grad(): | ||
| for data, target in test_loader: | ||
| data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device) | ||
| output = model(data) | ||
| test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() | ||
| pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True) | ||
| correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item() | ||
| test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset) | ||
| acc = 100 * correct / len(test_loader.dataset) | ||
|
|
||
| print('Loss: {} Accuracy: {}%)\n'.format( | ||
| test_loss, acc)) | ||
| return acc | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| def main(): | ||
| torch.manual_seed(0) | ||
| device = torch.device('cuda') | ||
| train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( | ||
| datasets.CIFAR10('./data.cifar10', train=True, download=True, | ||
| transform=transforms.Compose([ | ||
| transforms.Pad(4), | ||
| transforms.RandomCrop(32), | ||
| transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), | ||
| transforms.ToTensor(), | ||
| transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)) | ||
| ])), | ||
| batch_size=64, shuffle=True) | ||
| test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( | ||
| datasets.CIFAR10('./data.cifar10', train=False, transform=transforms.Compose([ | ||
| transforms.ToTensor(), | ||
| transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)) | ||
| ])), | ||
| batch_size=200, shuffle=False) | ||
|
|
||
| model = vgg() | ||
| model.to(device) | ||
|
|
||
| # Train the base VGG-16 model | ||
| print('=' * 10 + 'Train the unpruned base model' + '=' * 10) | ||
| optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=1e-4) | ||
| lr_scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, 160, 0) | ||
| for epoch in range(160): | ||
| train(model, device, train_loader, optimizer) | ||
| test(model, device, test_loader) | ||
| lr_scheduler.step(epoch) | ||
| torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'vgg16_cifar10.pth') | ||
|
|
||
| # Test base model accuracy | ||
| print('=' * 10 + 'Test on the original model' + '=' * 10) | ||
| model.load_state_dict(torch.load('vgg16_cifar10.pth')) | ||
| test(model, device, test_loader) | ||
| # top1 = 93.51% | ||
|
|
||
| # Pruning Configuration, in paper 'PRUNING FILTERS FOR EFFICIENT CONVNETS', | ||
| # Conv_1, Conv_8, Conv_9, Conv_10, Conv_11, Conv_12 are pruned with 50% sparsity, as 'VGG-16-pruned-A' | ||
| configure_list = [{ | ||
| 'sparsity': 0.5, | ||
| 'op_types': ['default'], | ||
| 'op_names': ['feature.0', 'feature.24', 'feature.27', 'feature.30', 'feature.34', 'feature.37'] | ||
| }] | ||
|
|
||
| # Prune model and test accuracy without fine tuning. | ||
| print('=' * 10 + 'Test on the pruned model before fine tune' + '=' * 10) | ||
| pruner = L1FilterPruner(model, configure_list) | ||
| model = pruner.compress() | ||
| test(model, device, test_loader) | ||
| # top1 = 88.19% | ||
|
|
||
| # Fine tune the pruned model for 40 epochs and test accuracy | ||
| print('=' * 10 + 'Fine tuning' + '=' * 10) | ||
| optimizer_finetune = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=1e-4) | ||
| best_top1 = 0 | ||
| for epoch in range(40): | ||
| pruner.update_epoch(epoch) | ||
| print('# Epoch {} #'.format(epoch)) | ||
| train(model, device, train_loader, optimizer_finetune) | ||
| top1 = test(model, device, test_loader) | ||
| if top1 > best_top1: | ||
| best_top1 = top1 | ||
| # Export the best model, 'model_path' stores state_dict of the pruned model, | ||
| # mask_path stores mask_dict of the pruned model | ||
| pruner.export_model(model_path='pruned_vgg16_cifar10.pth', mask_path='mask_vgg16_cifar10.pth') | ||
|
|
||
| # Test the exported model | ||
| print('=' * 10 + 'Test on the pruned model after fine tune' + '=' * 10) | ||
| new_model = vgg() | ||
| new_model.to(device) | ||
| new_model.load_state_dict(torch.load('pruned_vgg16_cifar10.pth')) | ||
| test(new_model, device, test_loader) | ||
| # top1 = 93.53% | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| if __name__ == '__main__': | ||
| main() |
Oops, something went wrong.