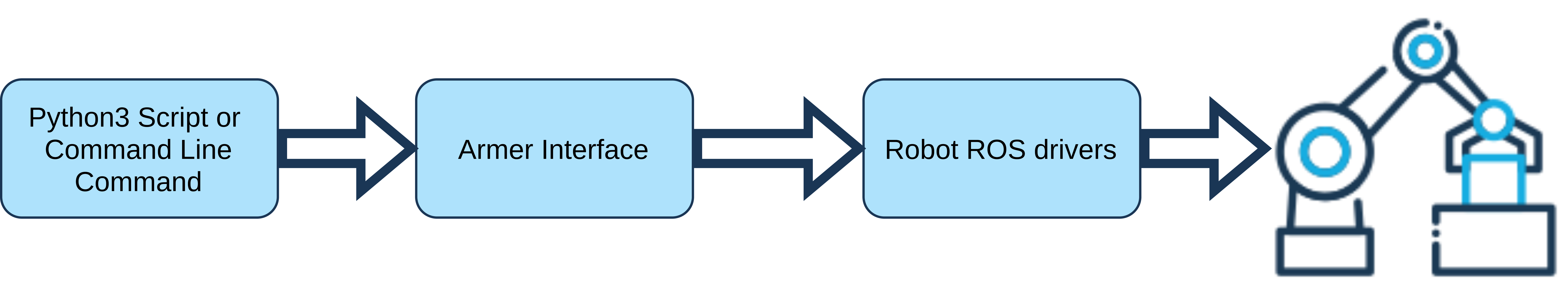
Armer aims to provide an interface layer between the hardware drivers of a robotic arm giving the user control in several ways:
- Joint velocity control
- Joint position control
- End effector Cartesian velocity control
- End effector Cartesian position control
In addition to a multiple control method layer, Armer is designed to be a compatability layer allowing the user to use the same code across different robotic platforms. Armer supports control for physical and simulated arms giving users the ability to develop even without access to a physical manipulator.
Below is a gif of 3 different simulated arms moving with the same cartesian velocity commands.
Several ROS action servers, topics and services are set up by Armer to enable this functionality. A summary of these can be found here.
Armer is built on the Python Robotics Toolbox (RTB) and requires a URDF loaded RTB model to calculate the required movement kinematics, RTB comes with browser based simulator Swift which Armer uses as an out of the box simulator.
Due to these supporting packages using Armer with a manipulator will require several requirements:
- Python >= 3.6
- ROS Noetic
- Robotics Toolbox for Python
- QCR repos
- Chrome browser (for using Swift sim)
- ROS drivers with joint velocity controllers
- Robotics Toolbox model
Copy and paste the following code snippet into a terminal to create a new catkin workspace and install Armer to it. Note this script will also add the workspace to be sourced every time a bash terminal is opened.
sudo apt install python3-pip pip install git+https://github.com/petercorke/spatialmath-python.git pip install git+https://github.com/jhavl/spatialgeometry.git pip install git+https://github.com/jhavl/swift.git pip install git+https://github.com/petercorke/robotics-toolbox-python.git mkdir -p ~/armer_ws/src && cd ~/armer_ws/src git clone https://github.com/qcr/armer.git && git clone https://github.com/qcr/armer_msgs cd .. && rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y catkin_make echo "source ~/armer_ws/devel/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc source ~/armer_ws/devel/setup.bash echo "Installation complete!"
Armer relies on the manipulator's ROS driver to communicate with the low level hardware so the the ROS drivers must be started along side Armer. NOTE: the below packages are required for control of a real robot - see below for simulation usage instructions
Currently Armer driver has packages that launches Armer and the target manipulator's drivers are bundled together. If your arm model has a hardware package, control should be a fairly plug and play experience. (An experience we are still working on so please let us know if it isn't.). Below are the github pages to arms with hardware packages. Install directions can be found on their respective pages.
-
Franka Panda: https://github.com/qcr/armer_panda
-
Universal Robot UR3: https://github.com/qcr/armer_ur
-
Universal Robot UR5: https://github.com/qcr/armer_ur
-
Universal Robot UR10: https://github.com/qcr/armer_ur
-
ABB IRB6700: https://github.com/qcr/armer_abb
For more information on setting up manipulators not listed here see the Armer documentation, Supported Arms.
The Armer interface can be launched with the following command for simulation:
roslaunch armer armer.launch config:={PATH_TO_CONFIG_YAML_FILE}
Alternatively, the Armer interface can be launched for a real robot using the following command (Note that this can also support simulation if you wish via the sim parameter):
roslaunch armer_{ROBOT_MODEL} robot_bringup.launch config:={PATH_TO_CONFIG_YAML_FILE} sim:={true/false}
After launching, an arm can be controlled in several ways. Some quick tutorials can be referenced below:
- Joint velocity control
- Joint position control
- End effector Cartesian velocity control
- End effector Cartesian position control
- End effector Cartesian velocity control with guarded motion
For more information and examples see the Armer documentation