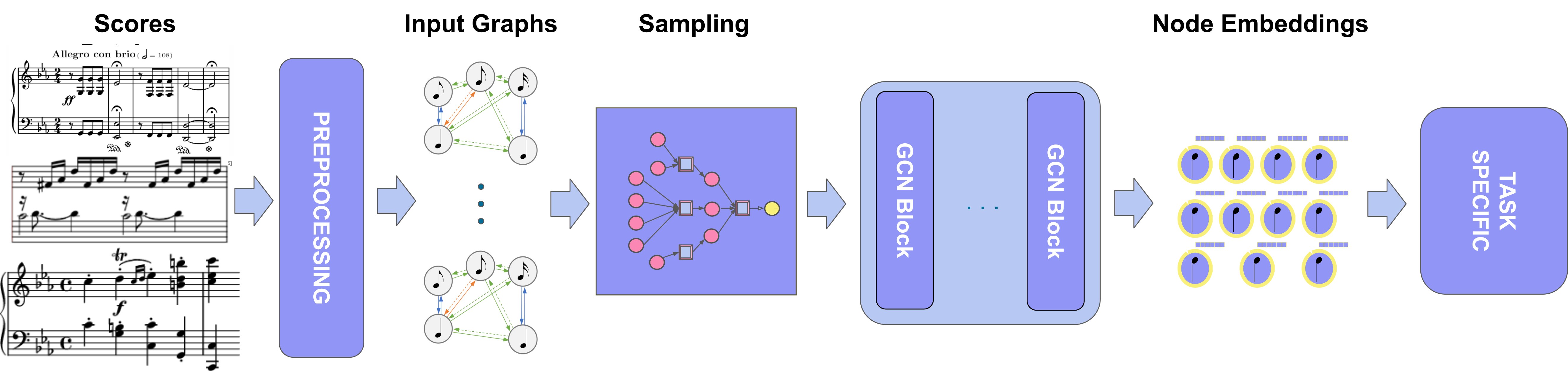
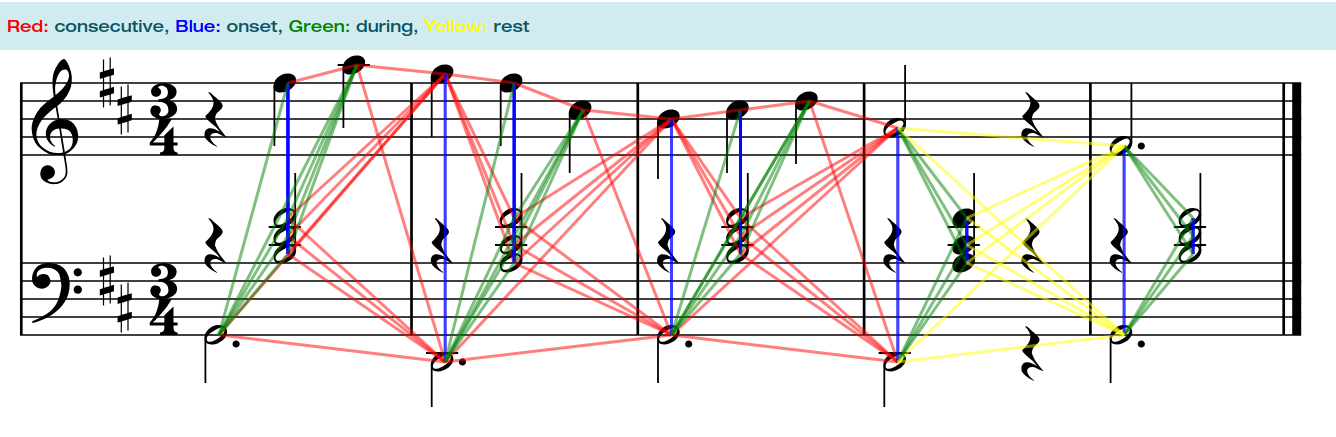
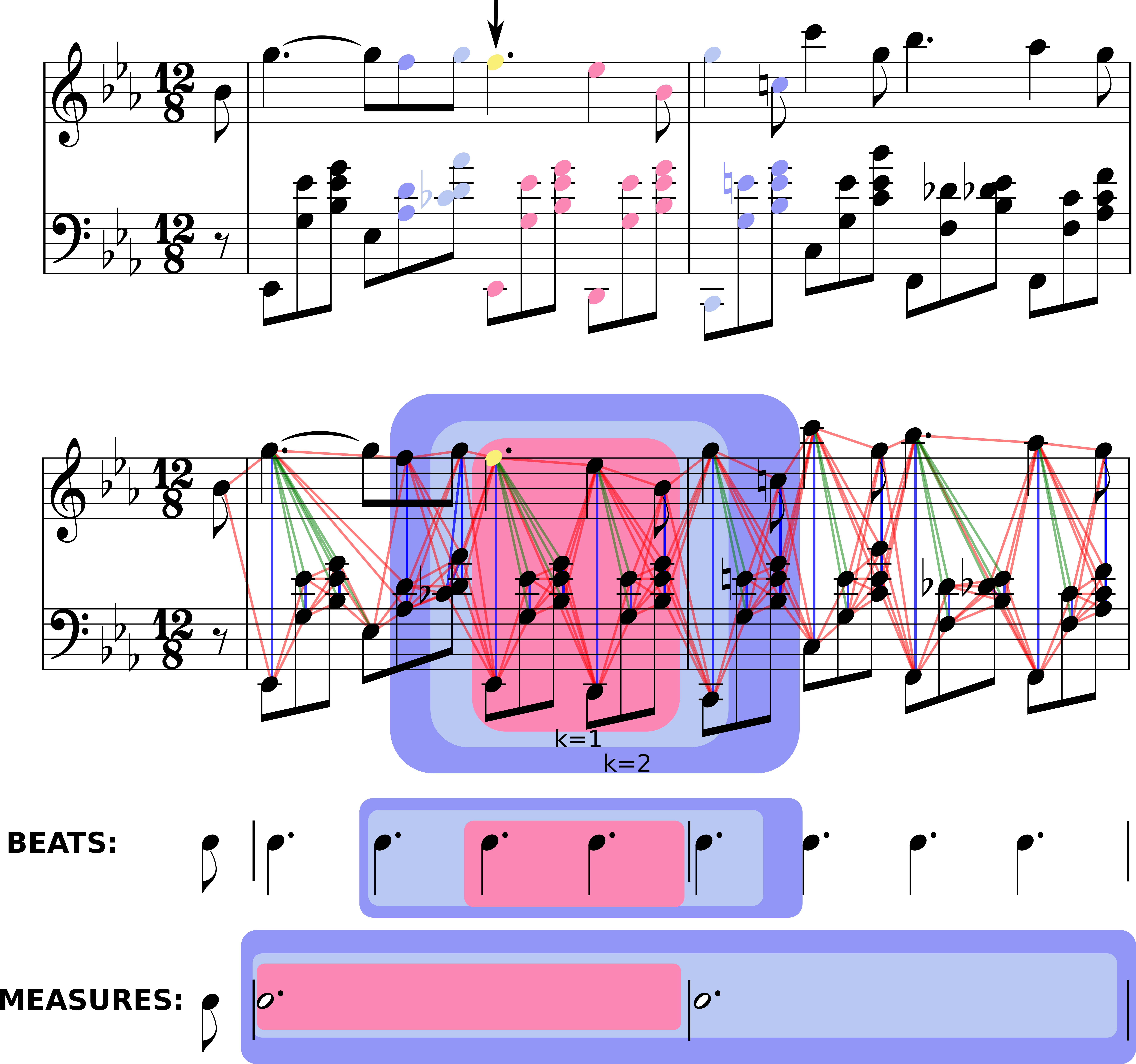
GraphMuse is a Python Library for Graph Deep Learning on Symbolic Music. This library intents to address Graph Deep Learning techniques and models applied specifically to Music Scores.
It contains a core set of graph-based music representations, based on Pytorch Geometric Data and HeteroData classes. It includes functionalities for these graphs such as Sampling and several Graph Convolutional Networks.
The main core of the library includes sampling strategies for Music Score Graphs, Dataloaders, Graph Creation classes, and Graph Convolutional Networks. The graph creation is implemented partly in C and works in unison with the Partitura library for parsing symbolic music.
It implements a variety of graph neural networks for music, including MusGConv, NoteGNN, MeasureGNn, BeatGNN, MetricalGNN, and HybridGNN.
Read the GraphMuse paper here.
GraphMuse is a library for symbolic music graph processing. It provides a set of tools for creating, manipulating, and learning from symbolic music graphs. It is built on top of PyTorch Geometric and provides a set of graph convolutional networks tailored to music data. GraphMuse is designed to be easy to use and flexible, allowing users to experiment with different graph representations and models for their music data.
GraphMuse aims to provide a set of tools for symbolic music graph processing that are easy to use and flexible.
GraphMuse is built on top of PyTorch and Pytorch Geometric. Therefore you need to install Pytorch and Pytorch Geometric first. We recommend to use conda or any other virtual environment to install and experiment with GraphMuse. GraphMuse is compatible with python 3.8 or later. To install a conda environment ensure that conda is installed in your system (info here) and then use:
conda install -n graphmuse python=3.11 pipFirst you need to install the Pytorch version suitable for your system. You can find the instructions here.
You also need to install Pytorch Geometric. You can find the instructions here. We recommend to use conda:
conda install pyg -c pygYou can install graphmuse along with the dependencies using pip:
pip install graphmuseIf you encounter problems during the installation due to missing the pyg-lib package you can install it using:
pip install pyg-lib -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-${TORCH}+${CUDA}.htmlby replacing your version of Torch and CUDA. To use CPU just type cpu. More info here.
Sometimes the optional dependencies of Pytorch Geometric that Graphmuse needs to work properly might cause problems due to C compilation or system compatibility. If you have problems with some of the torch scatter, sparse, cluster, or pyg-lib packages please follow the instructions here.
When encountering problems with some of these dependency packages usually the best solution is to start fresh with the installation.
You can also install GraphMuse from source. First, clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/manoskary/graphmuse.git
cd graphmuseThen use pip for the rest of the dependencies:
pip install --verbose git+https://github.com/pyg-team/pyg-lib.git
pip install --verbose torch_scatter
pip install --verbose torch_sparse
pip install --verbose torch_cluster
pip install partituraand install using the setup file:
python setup.py installThe GraphMuse processing pipeline:
GraphMuse includes a variety of graph convolutional layers for music graphs.
Using the MetricalGNN model a simple example of a forward pass is shown below.
import graphmuse.nn as gmnn
import torch
# Define the number of input features, output features, and edge features
num_input_features = 10
num_hidden_features = 10
num_output_features = 10
num_layers = 1
# metadata needs to be provided for the metrical graph similarly to Pytorch Geometric heterogeneous graph modules.
metadata = (
['note'],
[('note', 'onset', 'note')]
)
# Create an instance of the MetricalGNN class
metrical_gnn = gmnn.MetricalGNN(num_input_features, num_hidden_features, num_output_features, num_layers, metadata=metadata)
# Create some dummy data for the forward pass
num_nodes = 5
x_dict = {'note': torch.rand((num_nodes, num_input_features))}
edge_index_dict = {('note', 'onset', 'note'): torch.tensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4, 0]])}
# Perform a forward pass
out = metrical_gnn(x_dict, edge_index_dict)
print(out)GraphMuse includes accelerated implementations of graph creation for music scores.
You can create a score graph from a musicxml file using the Partitura Python Library and the create_score_graph function from GraphMuse.
import graphmuse as gm
import partitura
import torch
score = partitura.load_musicxml('path_to_musicxml')
note_array = score.note_array()
feature_array = torch.rand((len(note_array), 10))
score_graph = gm.create_score_graph(feature_array, note_array)
print(score_graph)A score graph is a PyTorch Geometric HeteroData object that follows the following conceptual structure:
GraphMuse includes a dataloader for sampling and batching music graphs together.
It uses the node-wise sampling strategy for each graph and batching them together.
You can specify the number of graphs to sample (batch_size) and the size of the subgraph to sample (subgraph_size).
Then, you can create an instance of the MuseNeighborLoader class by passing the list of graphs, the subgraph size, the batch size, and the number of neighbors as arguments.
Finally, you can iterate over the dataloader to get batches of subgraphs.
from graphmuse.loader import MuseNeighborLoader
from graphmuse.utils import create_random_music_graph
import numpy as np
import torch
# Create a random graph
num_graphs = 10
max_nodes = 200
min_nodes = 100
max_dur = 20
min_dur = 1
subgraph_size = 50
batch_size = 4
feature_size = 10
labels = 4
graphs = list()
for i in range(num_graphs):
l = np.random.randint(min_nodes, max_nodes)
graph = create_random_music_graph(
graph_size=l, min_duration=min_dur, max_duration=max_dur, feature_size=feature_size, add_beat_nodes=True)
label = np.random.randint(0, labels, graph["note"].x.shape[0])
graph["note"].y = torch.tensor(label, dtype=torch.long)
graphs.append(graph)
# Create dataloader
dataloader = MuseNeighborLoader(graphs, subgraph_size=subgraph_size, batch_size=batch_size,
num_neighbors=[3, 3, 3])
# Iterate over the dataloader
for batch in dataloader:
print(batch)The conceptual structure of sampling from each score graph is shown below:
GraphMuse was published at ISMIR 2024. To cite our work:
@inproceedings{karystinaios2024graphmuse,
title={GraphMuse: A Library for Symbolic Music Graph Processing},
author={Karystinaios, Emmanouil and Widmer, Gerhard},
booktitle={Proceedings of the International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR)},
year={2024}
}