To run this code, you need to open "Inspect Elements" section in your favorite browser and observe the results in JavaScript Console.
You can use this algorithm to find the shortest path in the graph, when you have to touch certain number of nodes. The perfect instance is a Grocery Store Map .
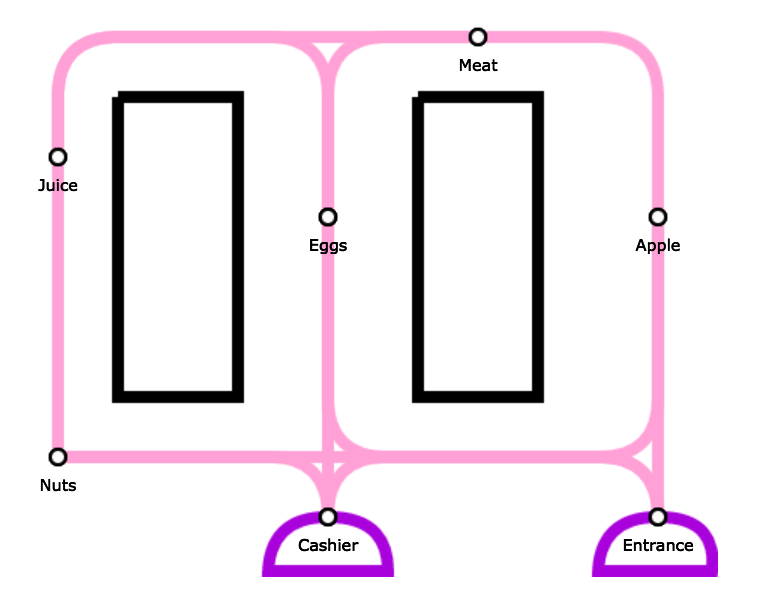
Imagine you need to purchase certain items in the grocery store and you like to know the shortest path to pick all the items. To make this happen, I modeled the store as a graph which is shown in the following picture:
In dik.js , Dijkstra's Algorithm and it's Graph are defined. Then in makeRoads.js , the graph can be implemented by adding edeges to each source node.
Following lines would implement the above graph:
makeRoads("start", "apple", 2, "eggs", 2, "nuts", 3, "end", 1);
makeRoads("apple", "meat", 1);
makeRoads("meat", "eggs", 1, "juice", 2);
makeRoads("eggs", "juice", 2, "end", 1, "nuts", 2);
makeRoads("juice", "nuts", 2);
makeRoads("nuts", "end", 1);The first argument of makeRoads function defines the source node and the following arguments, define the nodes that it is connected to and the weight of edges. You can make your own graph and decide how complex you want it to be.
At this current version of program , the desired items to buy, should be "hard coded". Therefore, you have can simply specify the items by making an array called "items" and modify that in the code.
//making an array of items
var items = ["meat","eggs","juice"];Then, if you run the code and check the JavaScript console, you see the order of the items in a way that you use shortest path to pick them all.
This program is the modified version of Dijkstra's algorithm taken from here .