Cookie Quick Manager: A complete manager for cookies accumulated during browsing. It allows you to view, edit, create, delete, backup, restore cookies and search them by domain names. Contextual Identities such as Private Browsing, First-Party Isolation, and SameSite flag are also supported. In addition, the LocalStorage of the page viewed can be deleted (see below).
Cookie Quick Manager is designed for developers, testers or people concerned about their privacy on the Internet.
This WebExtension is compatible with Firefox 57 and is inspired by addons like Cookies Manager+ and Advanced Cookie Manager whose development has been discontinued due to the withdrawal of the support for "Legacy" extensions.
November 2018: Cookie Quick Manager is now available on Android!
- User friendly: Clear and structured user interface. Each parameter and functionality is described when the mouse is over the element.
- Windowed and tab mode: Choose the opening in a tab to get a wider view.
- Transparency and security: The source code is free (under GPLv3) and # published on a public platform, the only way to allow reviews and external contributions.
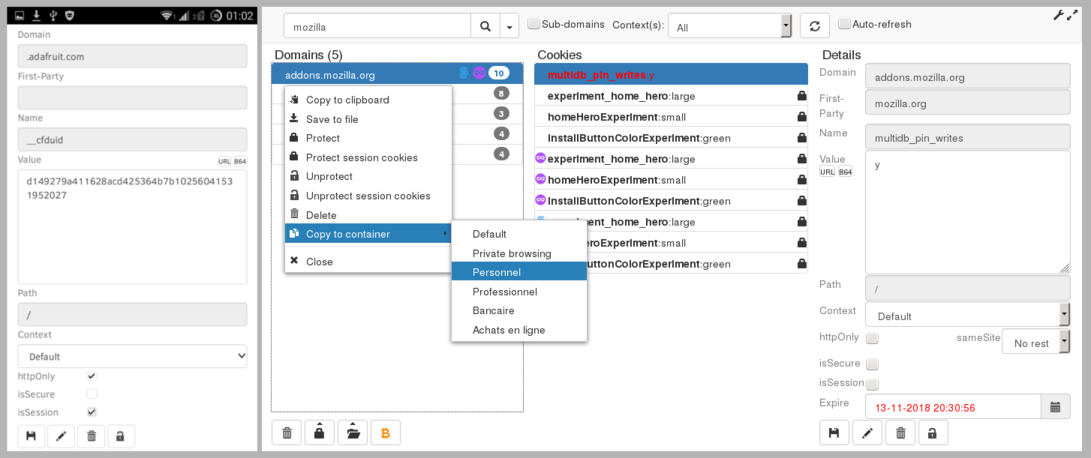
- Search: A user can search for cookies of a domain and subdomains which depend on it.
- Edit/Create: All the attributes of a cookie can be modified: domain, path, name, value, expiration date, as well as secure and httponly flags.
- Delete: Remove the cookies of the current website in two clicks.
- Export: The export and import of a cookie or cookies from a domain in JSON or Netscape format is just as easy.
- First-Party Isolation: Supported with some limitations (due to API bugs) on Firefox 59, 60, and 61, and without limitations on Firefox 62 (scheduled on September 2018).
- Contexts: Contexts (also called Multi-Account Containers, or Contextual Identities) are supported. A user can search and display cookies inside a container, or copy cookies from a container to another, or save a cookie in a specific context.
- SameSite: The SameSite flag is supported. This is a partial protection against the risks associated with Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) and Cross-Site Script Inclusion (XSSI) attacks, implemented since Firefox 63.
- Cookie protection: Delete cookies except protected ones, with two clicks at anytime from the website you are viewing. An option can also prevent cookies from being deleted by the sites themselves.
- Protection of session cookies: Session cookies can be protected in two clicks to prevent accidental logout from websites after cleaning normal cookies.
- Cleaning and privacy: Can automatically delete all cookies at startup.
- LocalStorage: Keys/values of the page viewed can be deleted.
This addon does not store or leak any personal information.
It requires the following permissions to operate:
- Host permission for all urls: This allows you to edit the cookies and to delete the Localstorage of any site visited.
- Cookies: Allows access to the browser's cookie store.
- ActiveTab: Allows access to the currently consulted url, and its favicon if it exists.
- Storage: Allows the storage of the following user settings:
- size of the windowed mode,
- protected cookies (only the name of the domains),
- the template used to import/export the cookies,
- the skin.
- Browsing data: Enables extensions to clear the data that is accumulated while the user is browsing (LocalStorage here).
- Contextual Identities: Allows the addon to list the containers.
- Privacy: Access and modify various privacy-related browser settings (the FirstPartyIsolation flag here).
- ClipboardWrite (optional): Allows the export of cookies to the clipboard from Firefox 63.
The protection of cookies is limited to the current addon actions, to the deletions that can be made by the sites themselves, or to the deletions made in the browser's "Cookies and Site Data" options. This means that if you choose the browser option to delete all cookies when it closes, the addon will be unable to restore them (the method used by the browser does not send the necessary signal to notify the addon). However, a similar option is reimplemented in the addon itself in order to keep only the protected cookies when restarting the browser.
This item allows a user to delete LocalStorage keys from the viewed page.
The LocalStorage is a quite new feature of HTML5 that allows developers to create data in your browser using JavaScript. Cookies are just one type of storage among others. You will also find the term "SessionStorage", a LocalStorage where data is stored temporarily (deleted on browser restart), but the important thing is that LocalStorage is persistent, and cleared only at the discretion of the visited websites. You may erase all of the LocalStorage store by following the procedure described in the documentation of Firefox, and by selecting "Offline Website Data".
From the point of view of privacy and security:
This kind of persistant data (even after clearing cache), was invented to store small data allowing the operation of online applications, but also offers new and better accurate ways of tracking thanks to the memorization of private or identifying data.
The extension is still in development with the launch of Firefox Quantum; questions, bug reports and feature requests are open on the GitHub repository.
-
You can contribute by reporting bugs or problems encountered by creating an issue on [this page] (https://github.com/ysard/cookie-quick-manager/issues)
-
You can translate the application into your language. The files are at this address: https://github.com/ysard/cookie-quick-manager/tree/fpi/src/_locales
You must fork the repository and then make a pull-request with your changes. See this documentation with illustrations:
- https://help.github.com/en/articles/fork-a-repo
- https://help.github.com/en/articles/creating-a-pull-request-from-a-fork
Then execute the following commands:
cd cookie-quick-manager
make get_missing_from_new_language LOCALE = "from"
(here, de is the locale code for Deutch language)
The previous command will create a file in src/_locales/<your_locale>/messages.json,
then display the list of elements to be translated.
The file does not need to be translated to 100% to be used!
You must then make your pull request on github.