Brief Project Description
In this project, we are trying to show a More Accurate & Near Real-time SentimentAnalysis on Tweets of Specific Topics.
This project, which combines sentiment analysis andclassification algorithm, will construct a classifier to classify the inputtweets (either collected from real-time twitter stream or entered manually bythe user) to three different categories (positive, neutral, negative) with atleast 2G data retrieved from twitter as training data.
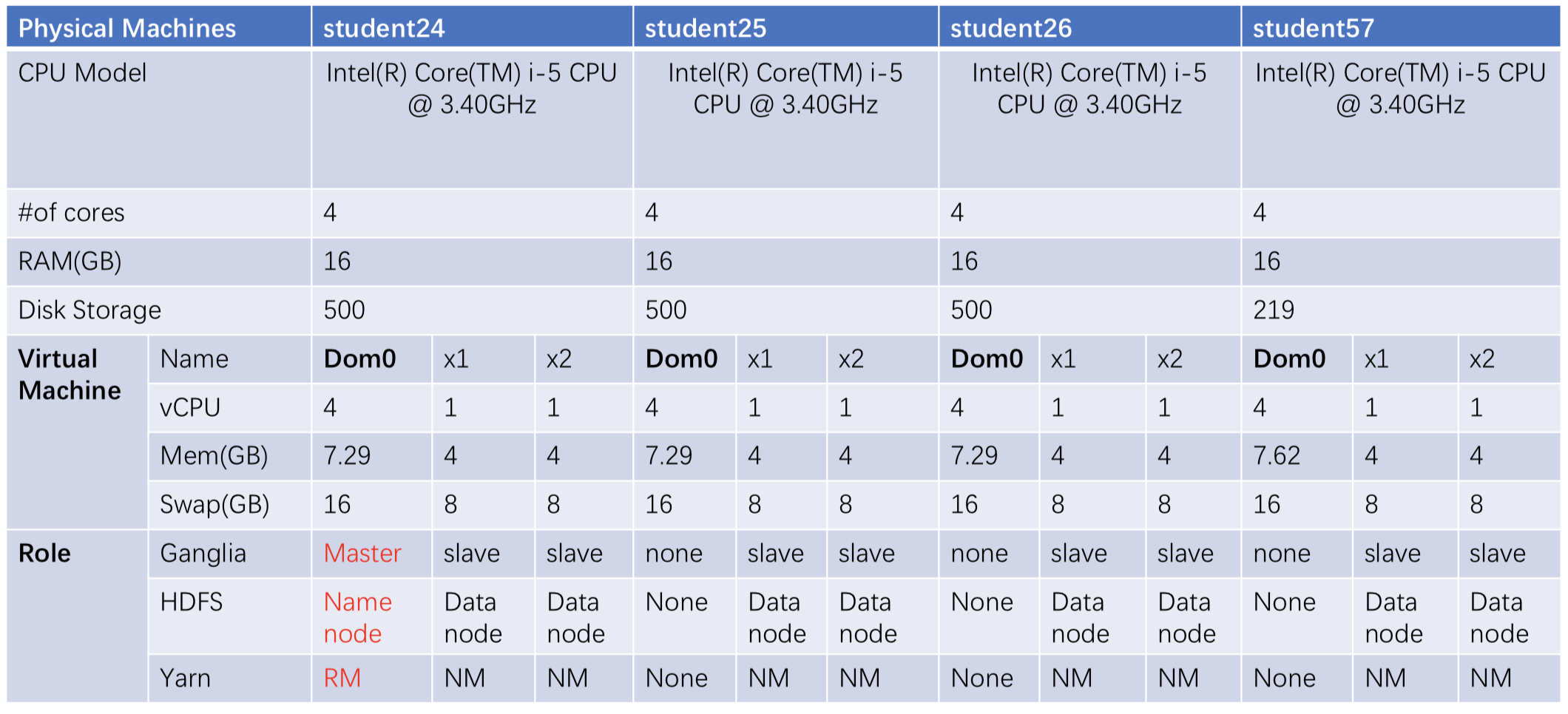
The training process will be performed on the COMP7305 cluster that was built before.
This project will also set up a web UI to demonstrate the classification result of sentiment analysis.
These instructions will let you apply the project and running on your machine for development and testing purposes.
Following cluster, tools and packages are required to run this project.
Hadoop
Spark
Hbase
The detailed steps of installing and configuring the cluster is introduced in the slides of COMP7305.
Java (Java8 has been installed in the previous cluster)
Python2
Python3
Javascript
HTML
CSS
pyspark
__future__
socket
json
re
numpy
string
textblob
time
collections
tweepy
flask
json
tweepy
psutil
time
datetime
os
sys
Python2.7.6 and Python3.4.3 are installed by default on ubuntu.Package Installation
$ pip install numpy
For more details about twitter data crawling api, please refer to Twitter Developer Docs
$ python3 get_tweets [user] [datatype] [nums_line] [nums_file]
e.g. $ python3 get_tweets Tom hist 100 3
which means use the auth key of Tom to get historical data, then write these data to the 3 files with 100 lines per file.
For example, the 2.2G data is stored in total.txt
The original data contains raw tweets, amount fo which is 2.2G.
The table **RawTweet **should be created in base. The the data can be written into hbase.
/opt/spark-2.2.1-bin-hadoop2.7/bin/spark-submit --master=yarn writeHbase.py
The module textblob will give the polarity of on tweet, value of which is between -1 and 1. We set the [-1, 0) as 2, 0 as 0 and (0, 1] as 1 respectively.
Therefor the processed polarity has three values (0, 1, 2).
- 0 means neutral sentiment
- 1means positive sentiment
- 2 means negative sentiment
After that, the program will construct json including "text", "polarity" and "id".
The table **RawTrainSet_Json_new **should be created in base. The the data will be cleaned and written into hbase.
/opt/spark-2.2.1-bin-hadoop2.7/bin/spark-submit --master=yarn RawTweetCleaner.py
Then, the training set has been prepared already.
Two models need to be trained, including the Word2vector and RandomForest
After the model is trained, it will be saved in the hdfs.
/opt/spark-2.2.1-bin-hadoop2.7/bin/spark-submit --master=yarn word_vector.py
After the model is trained, it will be saved in the hdfs.
/opt/spark-2.2.1-bin-hadoop2.7/bin/spark-submit --master=yarn sparkSA_partial.py
Firstly, the TweetRead.py should be executed. It is used to get real-time tweet from the API provided by Twitter. The data will be sent to SparkStreaming real-time through socket.
python3 TweetRead.py
Sencondly, the SparkStreaming.py is executed. The program will load the two models including Word2vector and RandomForest in initial steps.
The time window fo SparkStreaming is set as 10 senconds, meaning the program will collect all real-time tweets in 10 senconds. The model will **predict **the class of all tweets in 10 senconds, after which the original tweets and class label will be saved in txt file for presentation in Web UI.
/opt/spark-2.2.1-bin-hadoop2.7/bin/spark-submit --master=yarn SparkStreaming.py
The prediction.py is executed. The program will load the two models including Word2vector and RandomForest in initial steps. It call call the socket as server to receive the request and data from the Web backend. After receiving the data, the text will be given the class based on our trained RandomForest model and the class label will be returned to the Web backend.
/opt/spark-2.2.1-bin-hadoop2.7/bin/spark-submit --master=yarn prediction.py
Executing the main.py will start the web server and the web interface will be available.
-
For SparkStreaming, ajax in web font-end is used to read the file saved by SparkStreaming.py to show the original tweets and class label in the Web UI. The textarea of presentation will be refreshed periodicallly.
-
For InputText, the text users input wil be sent to back-end through post.
Then back-end use socket to transfer the data to the module InputText which will predict the class label of the tweet and return the class label to back-end.
The back-end transfer the class label to font-end to show the class label in Web UI.
python3 main.py