-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
Data flow
The widget-editor utilizes Redux and Redux-Saga for its internal data flow. Below you will find details about pieces of code that are relevant in the widget-editor.
- Store structure
-
@packages/widget-editor/sagas @packages/core/services/data@packages/core/services/state-proxy- Data flow schema
In the current store structure, each node has a specific purpose and we try to keep the node footprint small. There is only one node that gets modified by user input, configuration. Everything else in the store is managed by our @widget-editor/core services.
-
configuration- It gets modified on runtime, any user input or dynamic value will go in here.
- Our core services will serialize values here for the
onSaveprop callback.
-
editor- It holds the editor's data state, for example the dataset and its data, the widget, the fields, the layers, etc.
- It gets set on the initial load and it is updated if the widget's data changes or or the
datasetIdprop is updated.
-
theme- This is the current theme of the widget, the user can pass it as a prop to the editor to control the look of the editor.
- It only gets modified on the initial load.
-
widget- It contains the Vega schema generated by our core services.
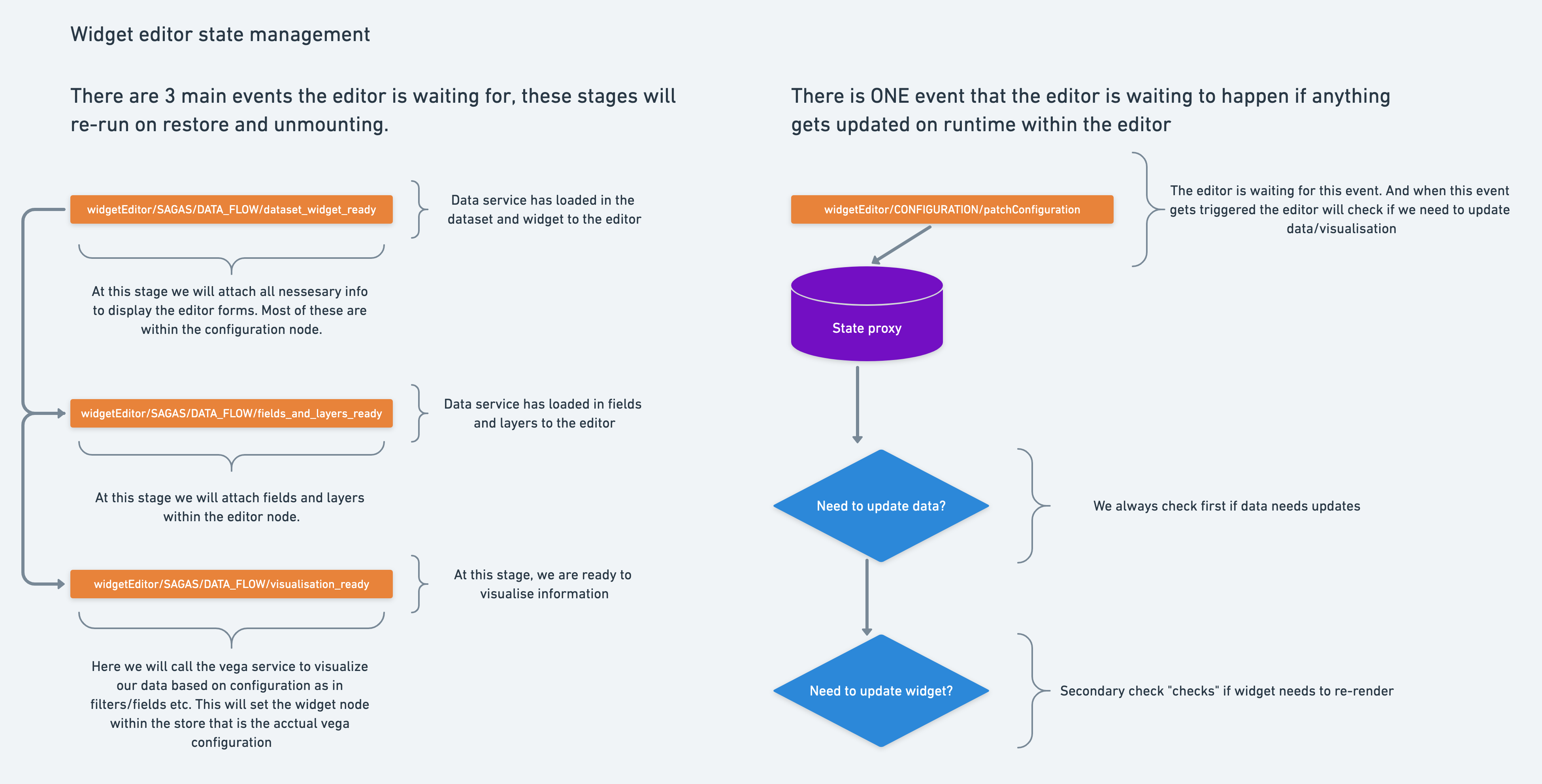
We currently have two sagas: editor and widget.
It is responsible for setting the initial state of the editor itself. It will wait for the DATA_FLOW_DATASET_WIDGET_READY event and set the configuration based on the widget. If no widget ID is provided to the widget-editor, a default widget structure is set.
It is responsible for managing the state of the widget editor and keeps the chart and chartData in sync.
-
It will wait for an initial render event called
DATA_FLOW_VISUALISATION_READYbefore rendering the chart. This is because we need initial data likedatasetandwidgetto know how to display the visualization. Within this saga, we are using aVegaServicethat translates the state of the store to a Vega specification. -
When anything gets modified within the editor,
patchConfigurationgets called. We will perform what we call a state sync using thestateProxy(explained below) that will check if anything was really updated, and perform any necessary updates using theVegaService.
This service is utilizing the provided adapter. You can read more about adapters on their dedicated page.
This service only has one task: to verify that the patchConfiguration events actually updated something in our store. If they did, it will request new data to the adapter and return its payload.
Whenever state flow changes are made, we make sure to not break the flow design. If we need to modify it, we must update the diagram to reflect the changes.
- Getting started
- User documentation
- Developer documentation